Large Anomalous Nernst Effect in a van der Waals Ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2
Anomalous Nernst effect (ANE), a result of charge current driven by temperature gradient, provides a probe of the topological nature of materials due to its sensitivity to the Berry curvature near the Fermi level. Of particular interest is the ANE in topological materials because the special band topology in these materials could introduce a very large ANE.
C. L. Chien (Johns Hopkins University)
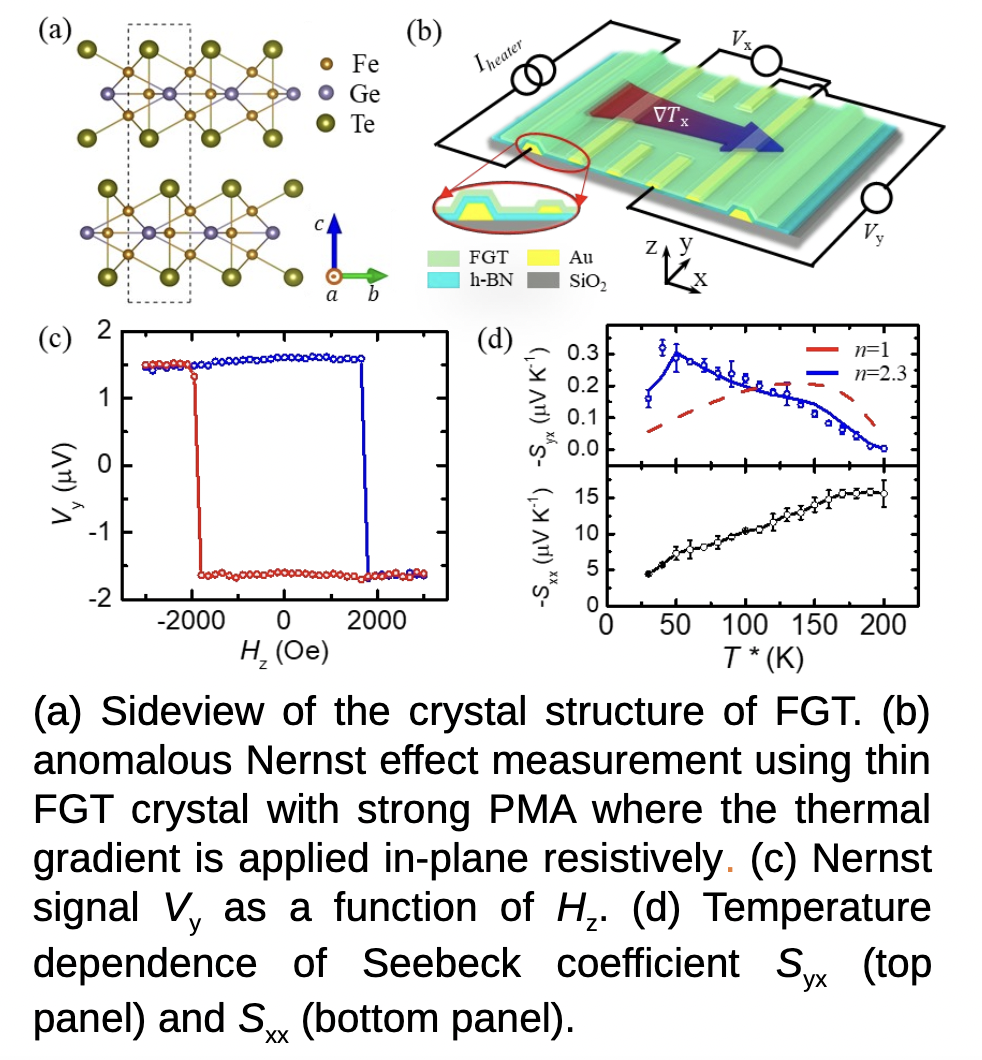
Anomalous Nernst effect (ANE), a result of charge current driven by temperature gradient, provides a probe of the topological nature of materials due to its sensitivity to the Berry curvature near the Fermi level. Of particular interest is the ANE in topological materials because the special band topology in these materials could introduce a very large ANE.
Fe3GeTe2 (FGT), one important member of the recently discovered two-dimensional van der Waals magnetic materials, offers a unique platform for ANE because of its metallic and topological nature. Here, we report the observation of large anomalous Nernst effect in FGT caused by a large Berry curvature near the Fermi level. Our work provides evidence of FGT as a topological ferromagnet and demonstrates the feasibility of using two-dimensional magnetic materials and their band topology for spin caloritronics applications.