Research Highlights
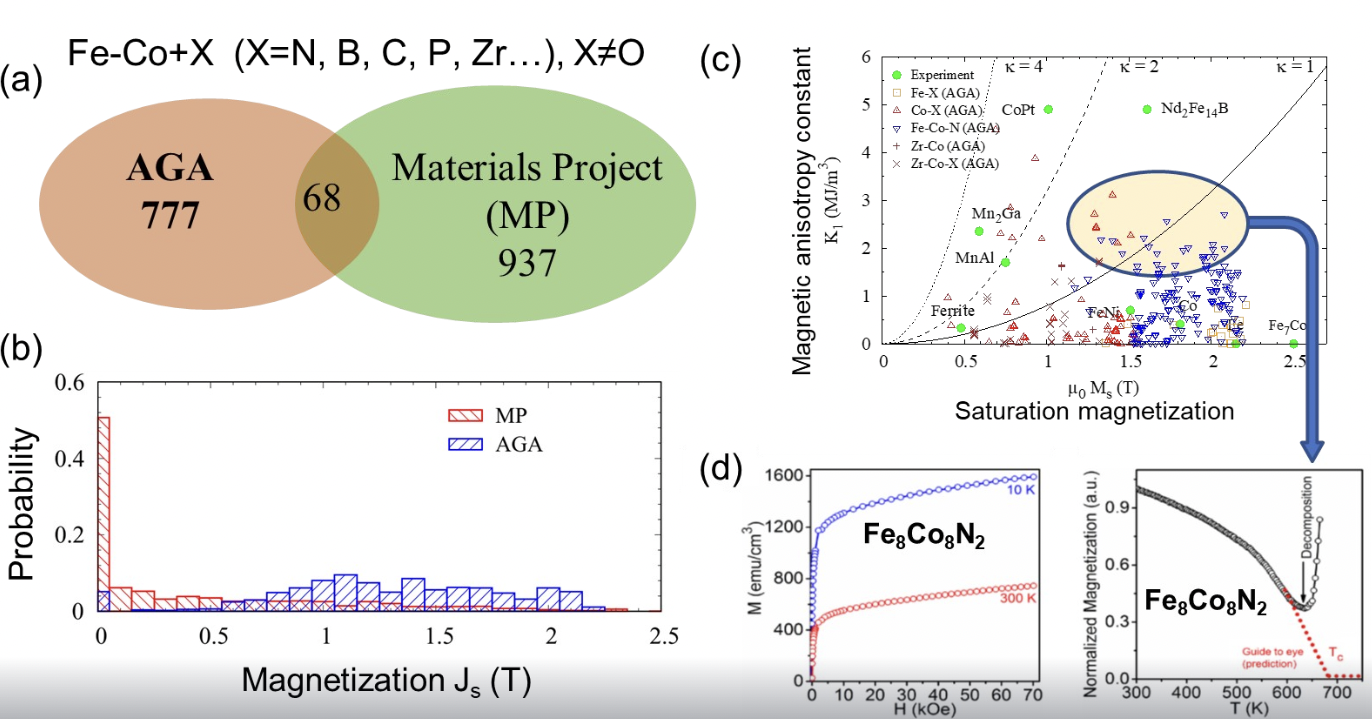
Discovering Rare-earth-free Magnetic Materials
10/14/2022 | J. Chelikowsky , K. Ho, C. Wang, D. Sellmyer, X. Xu
An open-access database is designed to facilitate machine learning.
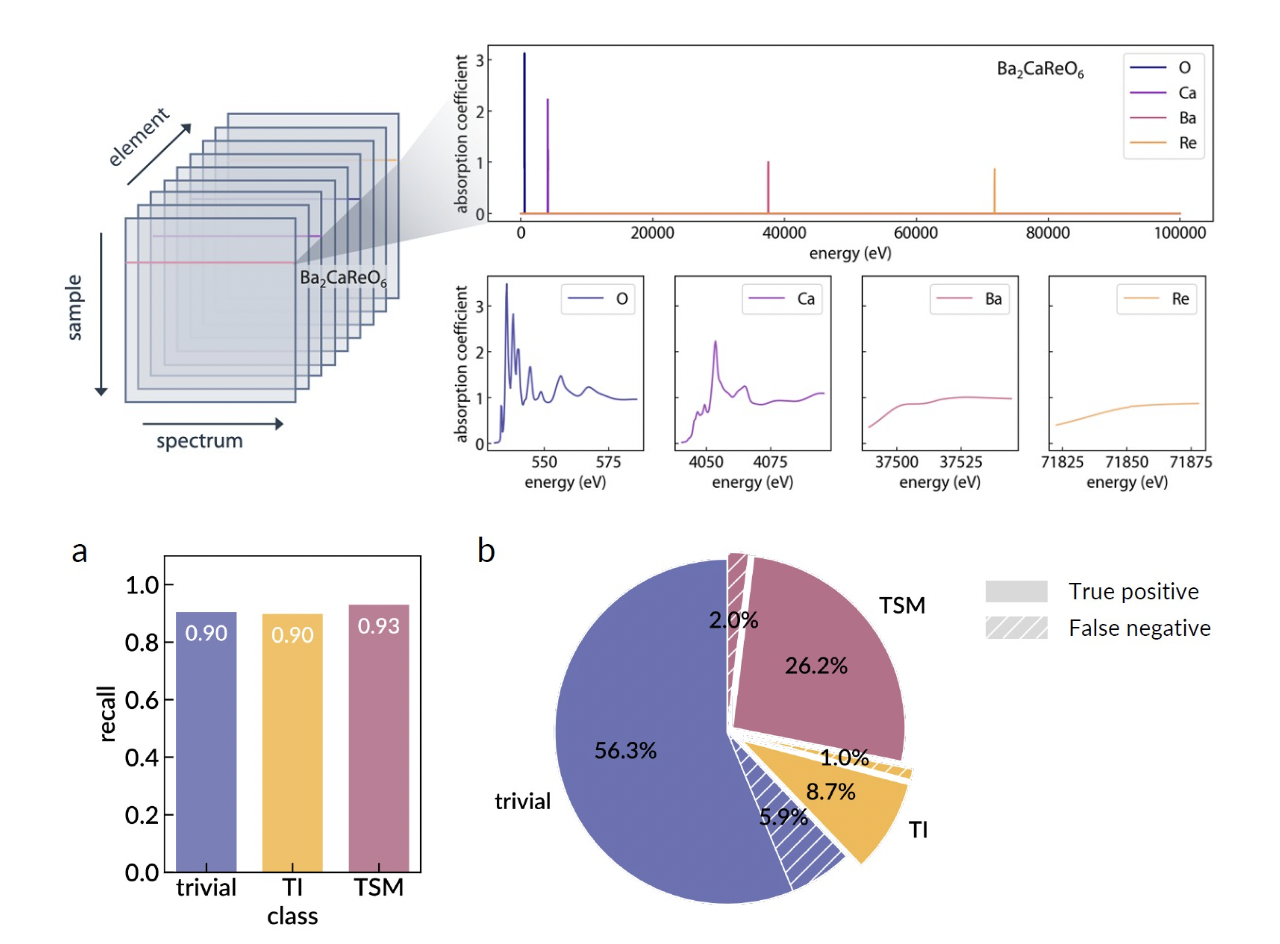
Machine-learning Spectral Indicators of Topology
10/1/2022 | Mingda Li, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Topological materials are promising for next-generation energy and information applications. However, the experimental determination of topology can be painstaking, with a few limitations such as limited sample types, high technical barriers, and limited sample environment.
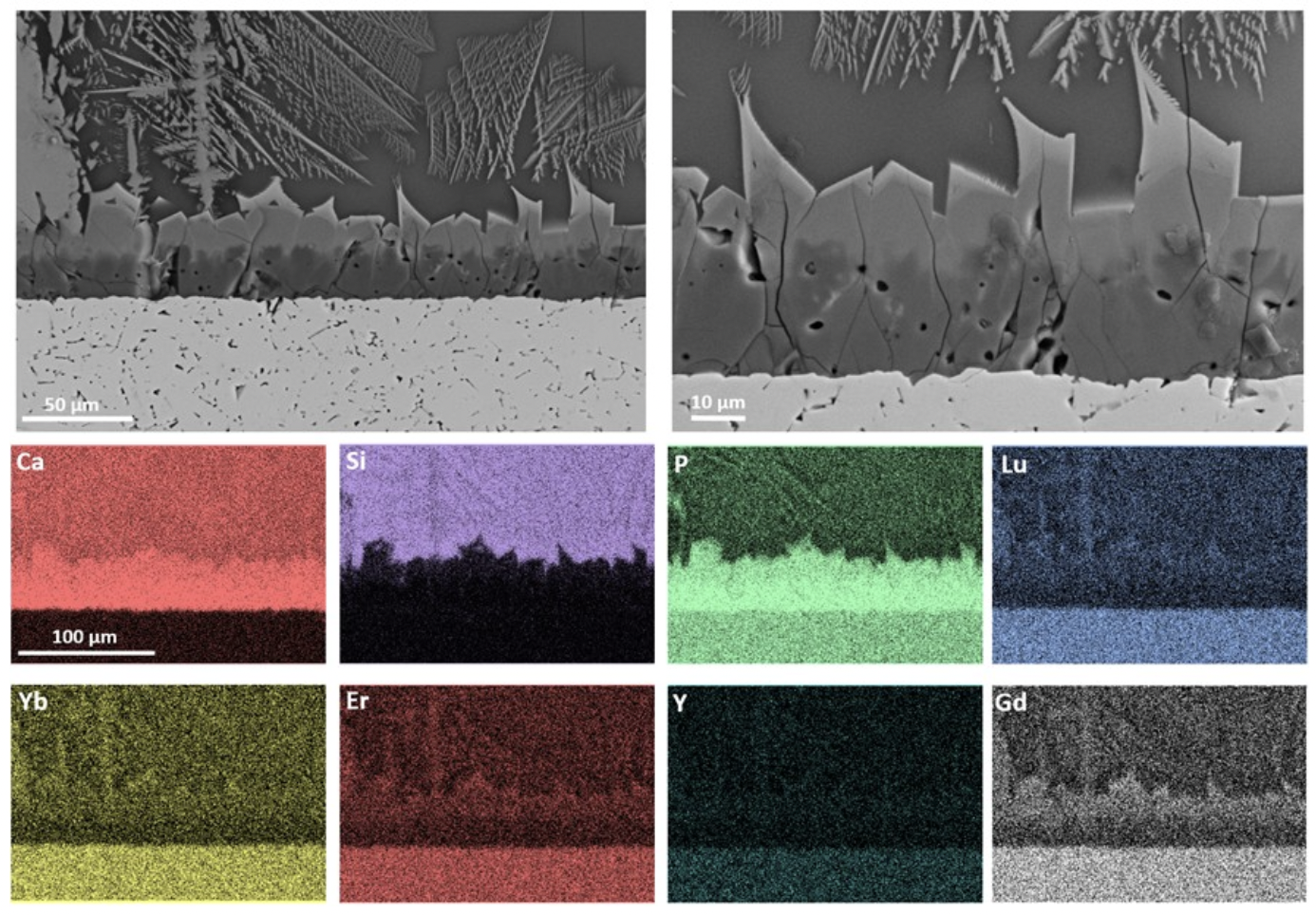
Machine Learning Accelerated Design and Discovery of Rare-earth Phosphates as Next Generation Environmental Barrier Coatings
9/24/2022
Researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute synthesized single phase multiple component rare-earth phosphate as potential environmental barrier coatings of structure materials for space and aerospace application.
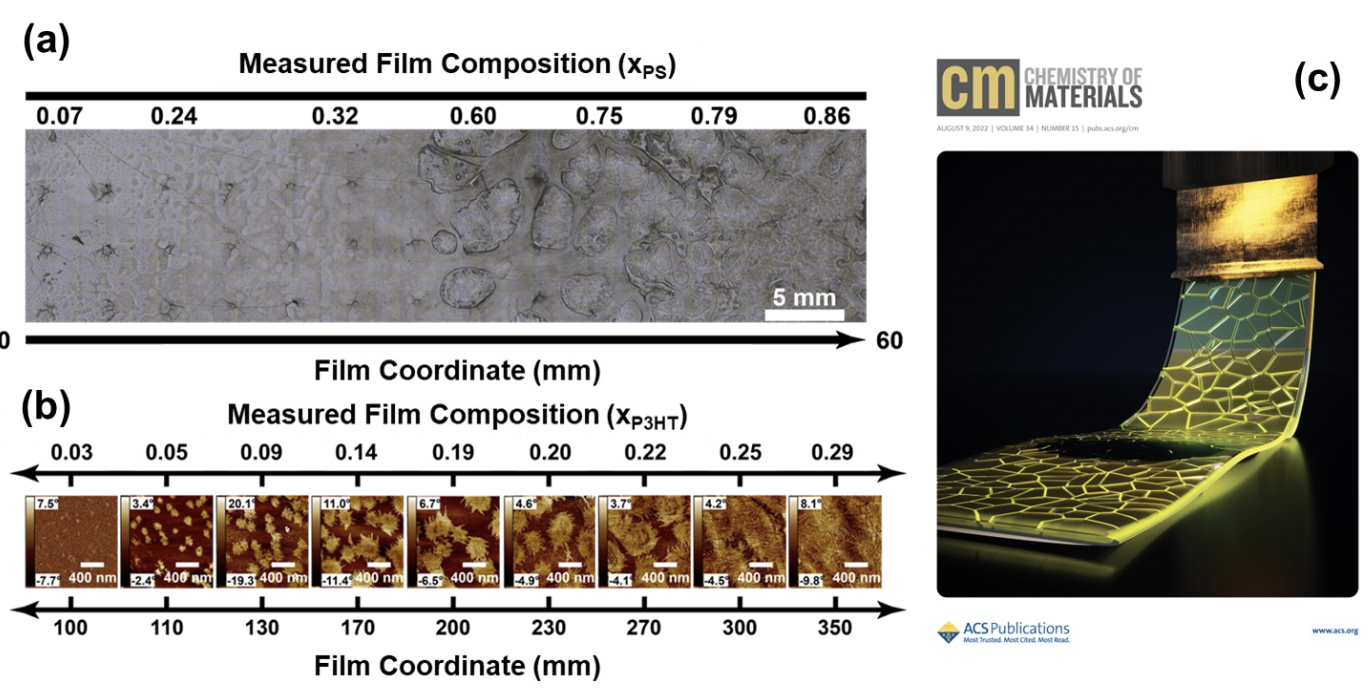
Composition Gradient High-Throughput Polymer Libraries Enabled by Passive Mixing and Elevated Temperature
7/1/2022
High-throughput experimentation (HTE) methods are key to enabling informatics-driven workflows to accelerate discovery of high-performance multicomponent materials. Here, we designed a solution coating system able to operate at temperatures over 110 °C to deposit composition gradient polymer libraries. The methodology provides an avenue for efficiently screening multiparameter spaces of a wide range of materials relevant to today’s applications.
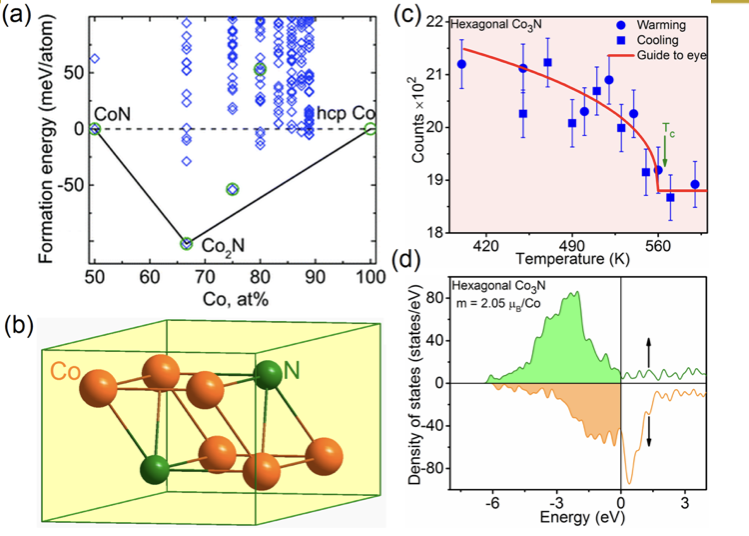
Creating Novel Magnetic Compounds with Complementary Experimental and Computational Methods
6/14/2022 | J. Chelikowsky, K. Ho, C. Wang, D. Sellmyer, X. Xu
The search for new magnetic materials with high saturation magnetic polarization (Js), magnetocrystalline anisotropy (K1), and Curie temperature (Tc) is important for a wide range of applications including information and energy processing.

Machine Learning on a Robotic Platform for the Design of Polymer-Protein Hybrids
6/11/2022 | Adam Gormley, Michael Webb
Polymer–protein hybrids are intriguing materials that can bolster protein stability in non-native environments, thereby enhancing their utility in diverse medicinal, commercial, and industrial applications
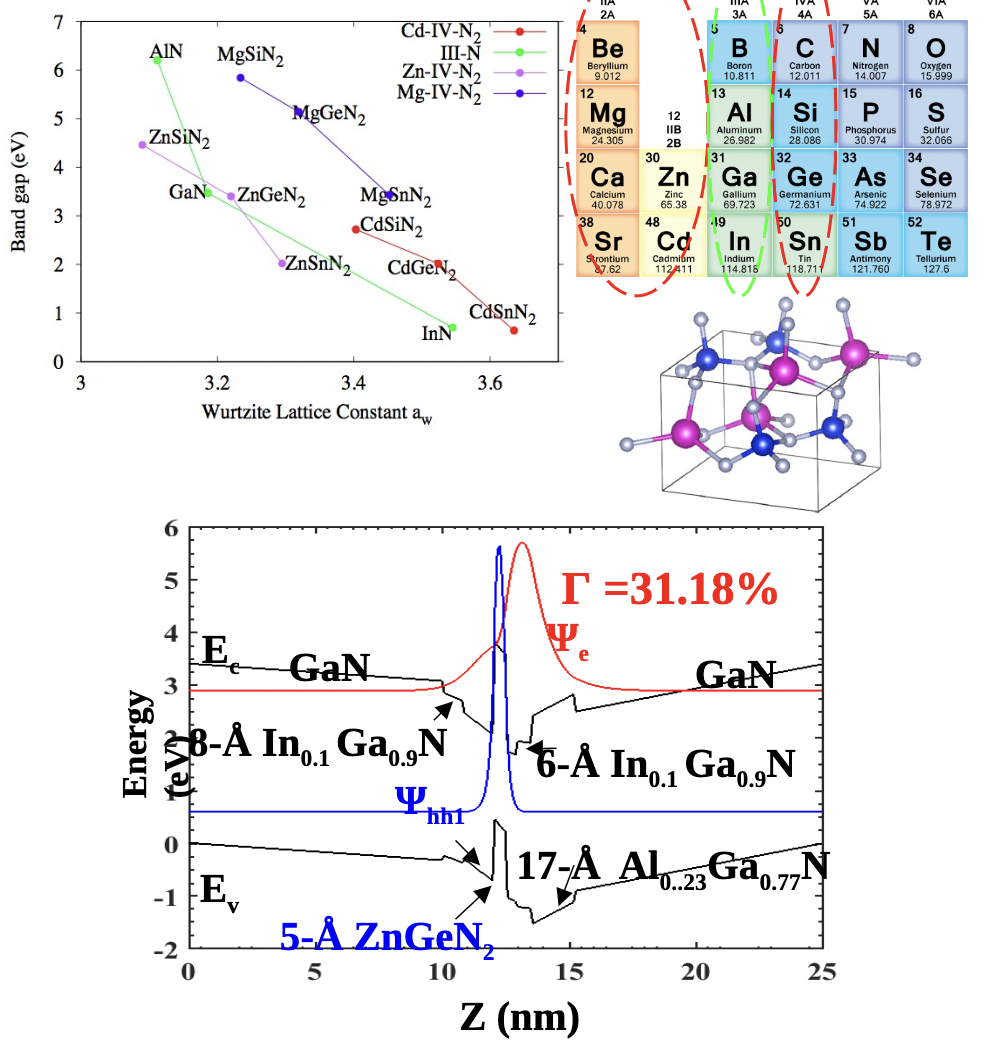
Nitride Semiconductor’s Family Expanded
5/16/2022 | K. Kash, H. Zhao, W. Lambrecht
The group III-nitrides (Al,Ga,In)N form the basis for the white LED lighting revolution, honored with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2014.
Room-temperature Superfluorescence in Hybrid Perovskites
3/31/2022 | F. So, K. Gundogdu (NC State U.)
Semiconducting perovskites that exhibit superfluorescence at room temperature do so through built-in thermal “shock absorbers” which protect dipoles within the material from thermal interference.
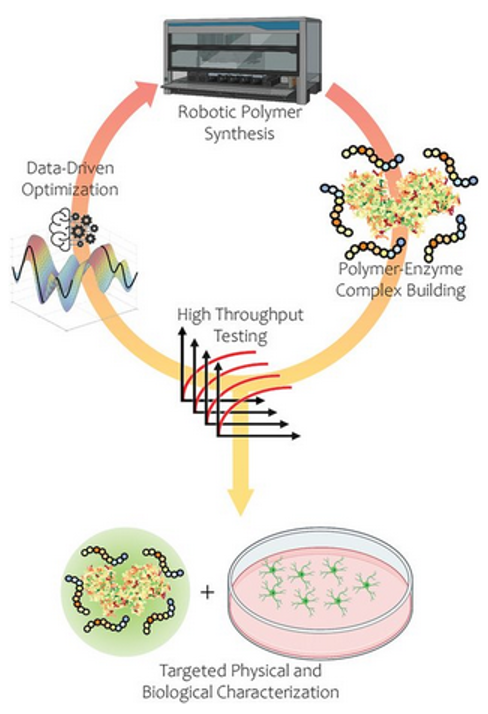
Machine-assisted Discovery of Polymer-enzyme Complexes for Sustained Neural Regeneration
3/18/2022 | Adam Gormley and Michael Webb (Rutgers University)
Among the many molecules that contribute to glial scarring, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are known to be potent inhibitors of neuronal regeneration. Chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) degrades the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) side chains of CSPGs and promotes tissue regeneration. However, ChABC is thermally unstable and loses all activity within a few hours at 37 °C.

Theory-guided Discovery of New Two-dimensional Metal-Chalcogenide Alloys with Exceptional Electrocatalytic Activity
1/1/2022 | Amin Salehi Khojin and Robert Klie (University of Illinois Chicago) and Rohan Mishra (Washington University)
We report the synthesis of new two-dimensional binary alloys of transition-metal dichalcogenides. Some of these alloys show outstanding performance as electrocatalyst in Li-air batteries and for the reduction of CO2.
Showing 141 to 150 of 217