Research Highlights
Excitonic Effects at the Direct Bandgap of Germanium
1/1/2022 | J. Menéndez, Arizona State University
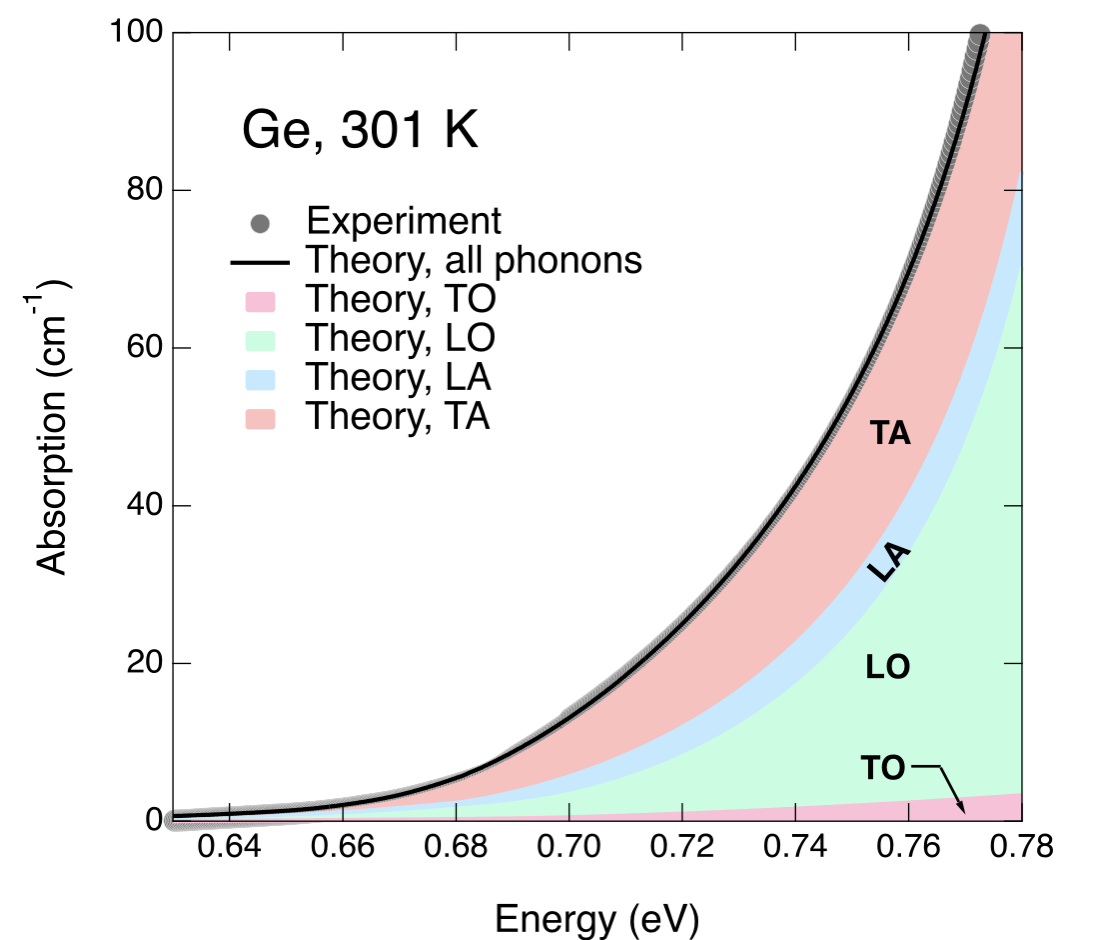
The divergence of the indirect absorption leads to the paradoxical conclusion that in the immediate vicinity of the direct gap, indirect absorption could become stronger than direct absorption. Eliminating this inconsistency requires a new theory of indirect absorption, which is one of the primary goals of this DMREF project.
Ultra-low Temperature Synthesis of Ge-based Optical Materials and Devices on Si using GeH3Cl
1/1/2022 | J. Menéndez, J. Kouvetakis (Arizona State University)
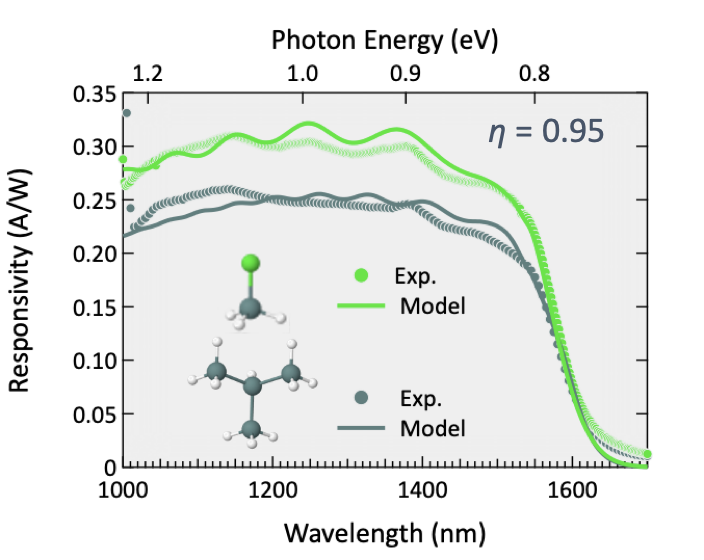
To demonstrate the quality of the Ge layers grown via the chlorogermane route, we fabricated pin diodes and measured their I-V characteristics and optical responsivity and found them to be comparable or better to those obtained with alternative low-temperature precursors. This bodes well for the use of chlorogermane in industrial efforts to integrate Ge functionalities with silicon CMOS.
An AI-driven Workflow for Accelerated Morphology, Electronic Structure, and Phase Characterization
1/1/2022 | Sarbajit Banerjee, Texas A&M University
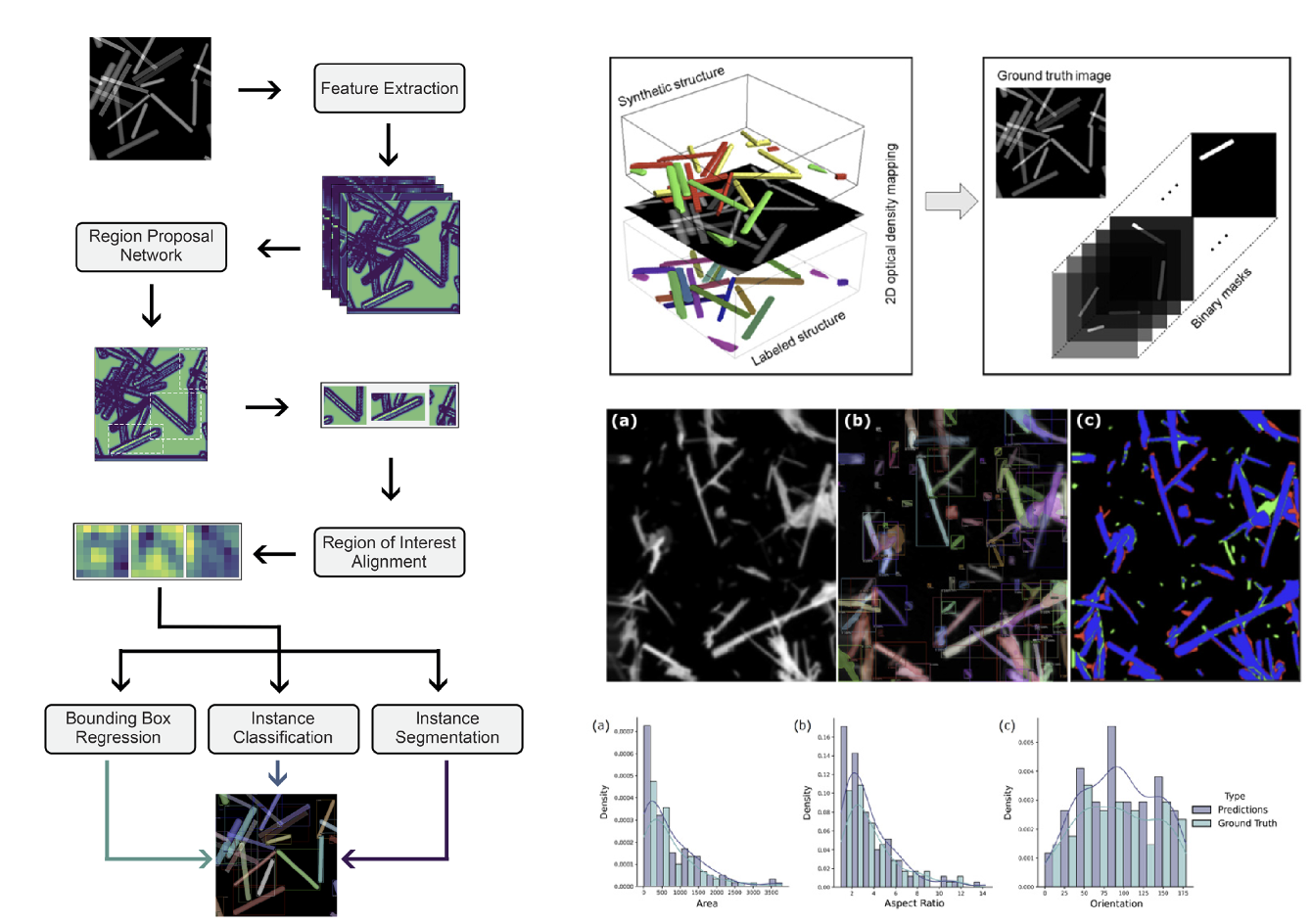
We have devised a workflow for deep learning of feature dimensions across electron microscopy, X-ray microscopy, and X-ray ptychography data.
New Topology & Tunable Superconductivity in a-Bi4I4
11/16/2021 | R.J. Birgeneau (Berkeley), C. N. Lau (Ohio St.),B. Lv, F. Zhang (UT-Dallas), M. Yi (Rice)
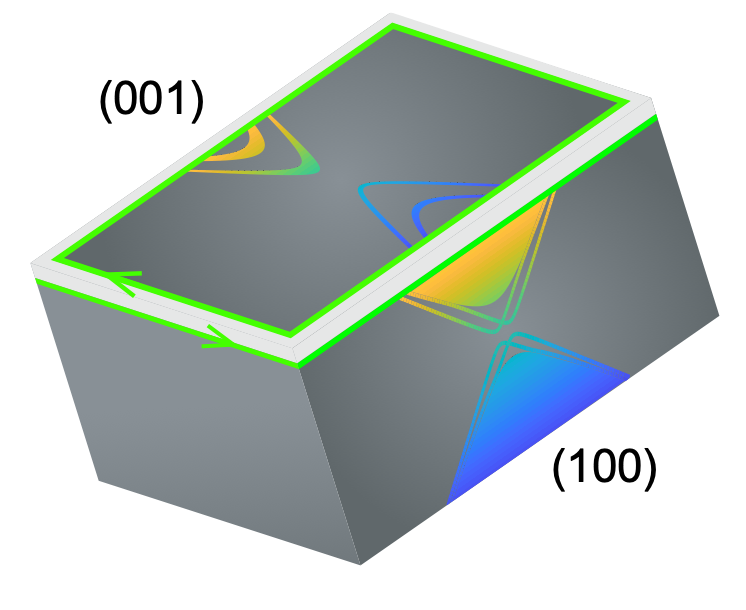
Given that 𝜷-Bi4I4 is the first weak topological insulator (TI) (identified by us, but not shown here), that 𝜶-Bi4I4 is a prototype higher-order TI (highlighted here), and that there is a room-temperature transition between the two structural phases (also identified by us, but not shown here), we have established a new (quasi-1D) TI paradigm that unifies the first and second order topological insulators.

Enhanced Room Temperature Infrared LEDs
11/12/2021
Plasmonic-enhanced emission has been moved toward practical application by the demonstration of an electrically pumped light emitting diode (LED) whose emission properties far exceed state-of-the-art.
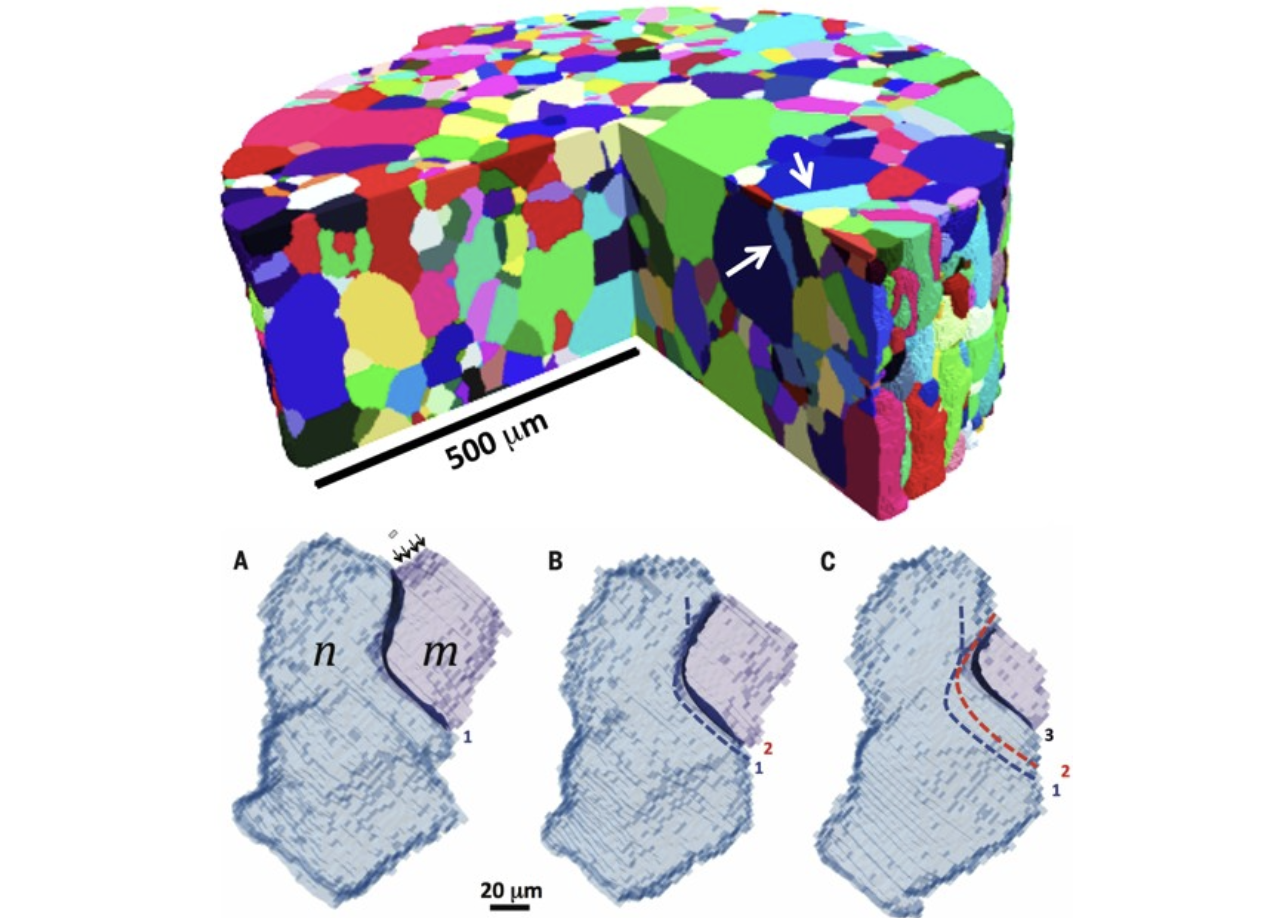
Grain Boundary Velocity and Curvature are Not Correlated
10/7/2021 | Gregory Rohrer , Robert Suter
To the eye, most common metals and ceramics used in commercial products appear to be uniformly solid. But at the microscopic level, they are polycrystalline, made up of aggregates of grains that have different sizes, shapes, and crystal orientations.
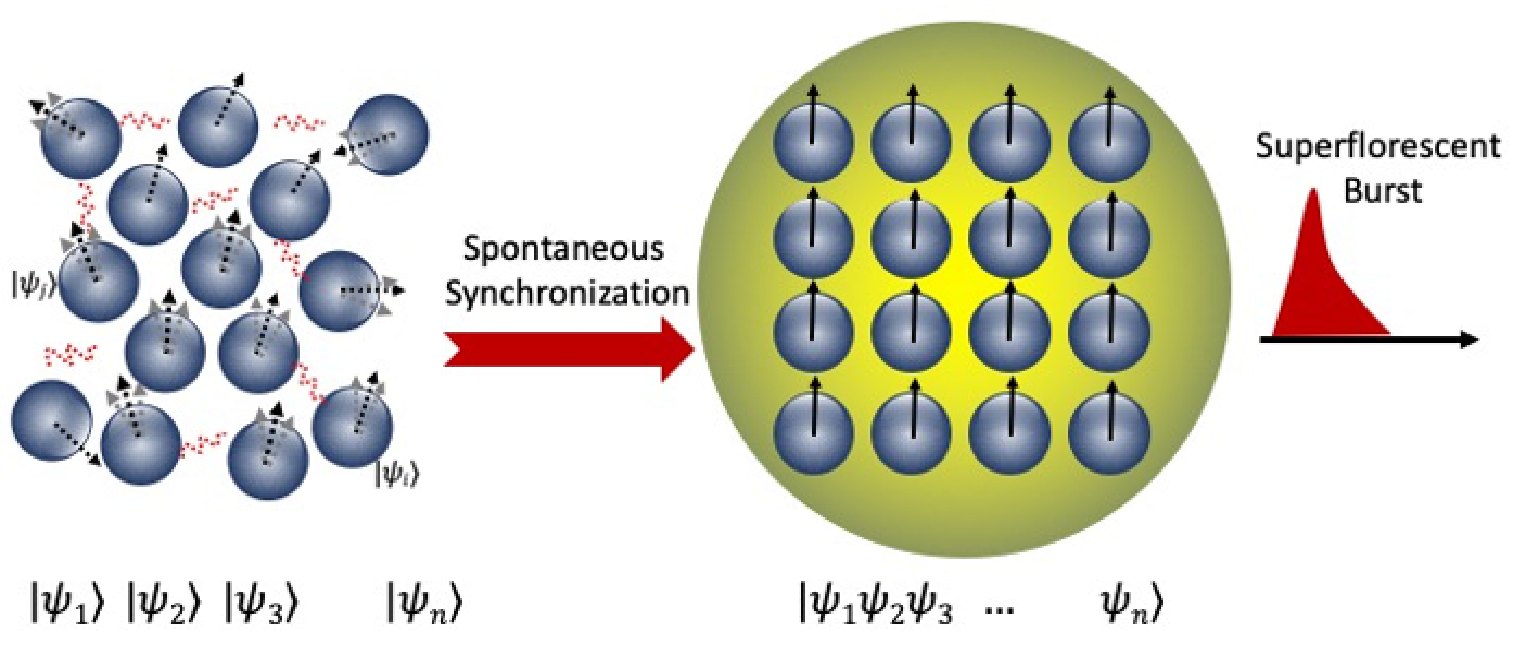
Common Perovskite Superfluoresces at High Temperatures
6/21/2021 | Franky So and Kenan Gundogdu (North Carolina State University)
Results of this study show that the creation and manipulation of collective coherent states in hybrid perovskites can be used as the basic building blocks for quantum applications.
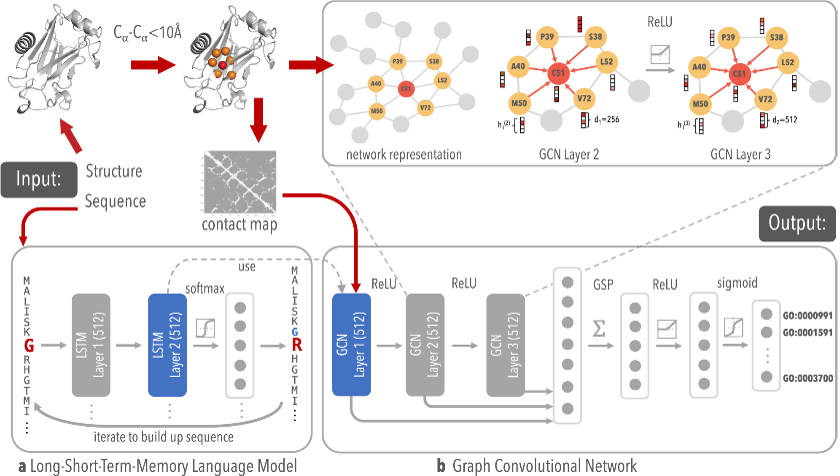
Computationally Driven Genetically Engineered Materials
5/26/2021 | J. Montclare, R. Bonneau, Y. Wadghiri (NYU)
Development of protein biomaterials that are capable of self-assembly into hydrogels has potential in biomedical applications including drug delivery and tissue engineering. A two-stage architecture, called DeepFRI, has been recently developed where functional salinity is established by training its algorithm on annotated structures from PDB and SWISS-MODEL and applying weighted class activation mapping of residues that are critical to function.
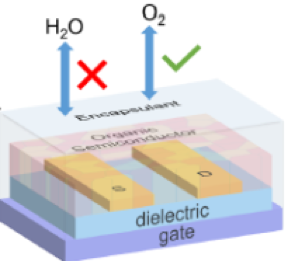
A New Pathway to Stable, Low-cost, Flexible Electronics
4/21/2021 | C. Risko, J. Anthony (U. Kentucky) and Jurchescu (Wake Forest)
While progress in material and device design has been astonishing, low environmental and operational stabilities remain longstanding problems obstructing their immediate deployment in real world applications.
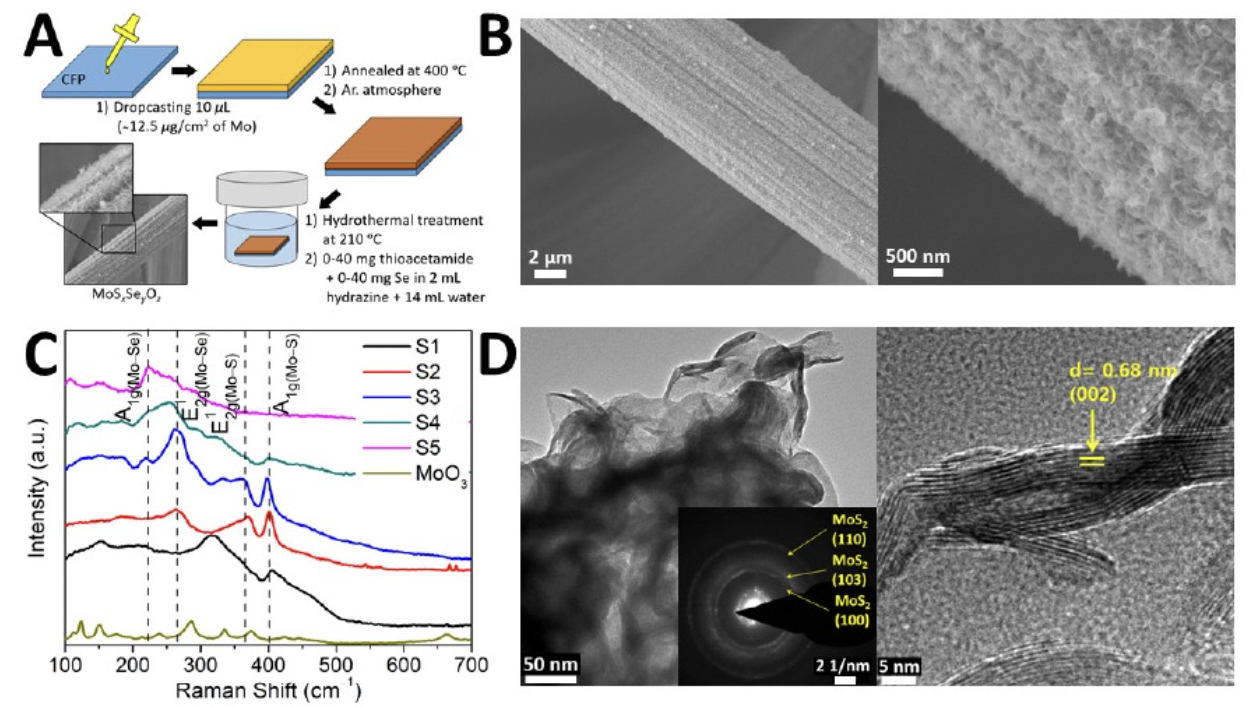
Enhancing the Electrocatalytic Activity of Molybdenum Disulfide
3/9/2021 | Sarbajit Banerjee
A) Illustration of the step-wise synthetic process comprising drop-casting, thermal annealing, and hydrothermal sulfidation/selenization used to grow MoS2-xSex/MoO3 nanosheets on carbon fiber paper. (B) SEM image of sample where Se:S=0.48 showing the homogeneous distribution of the nanosheets on carbon filter paper. (C) Raman spectra (514.5 nm excitation) acquired for MoS2-xSex/MoO3 samples with increasing concentration of Se. (D) Low-magnification and HRTEM images of a sample with a Se:S ratio of 0.62 illustrating the layered structure of MoS2/MoSe2. The left inset shows a SAED pattern of the chalcogenide layers.
Showing 151 to 160 of 217