Research Highlights
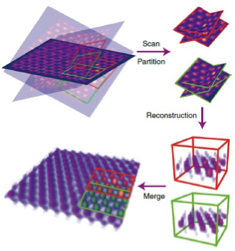
3D Map of Atoms in 2D Materials
8/8/2024 | Jianwei Miao (UCLA)
Reliable deployment in applications of graphene and other two-dimensional (2D) materials requires a complete understanding, at the atomic level, of the nature of defects that can significantly affect their physical properties.

Understanding Tooth Enamel Degradation
8/8/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder)
Degradation of tooth enamel leading to dental cavities is a common health concern as 32% of the worlds’ adult population has had cavities at some time in their lives. Zinc and stannous ions are commonly used in oral care to reduce tooth enamel degradation.
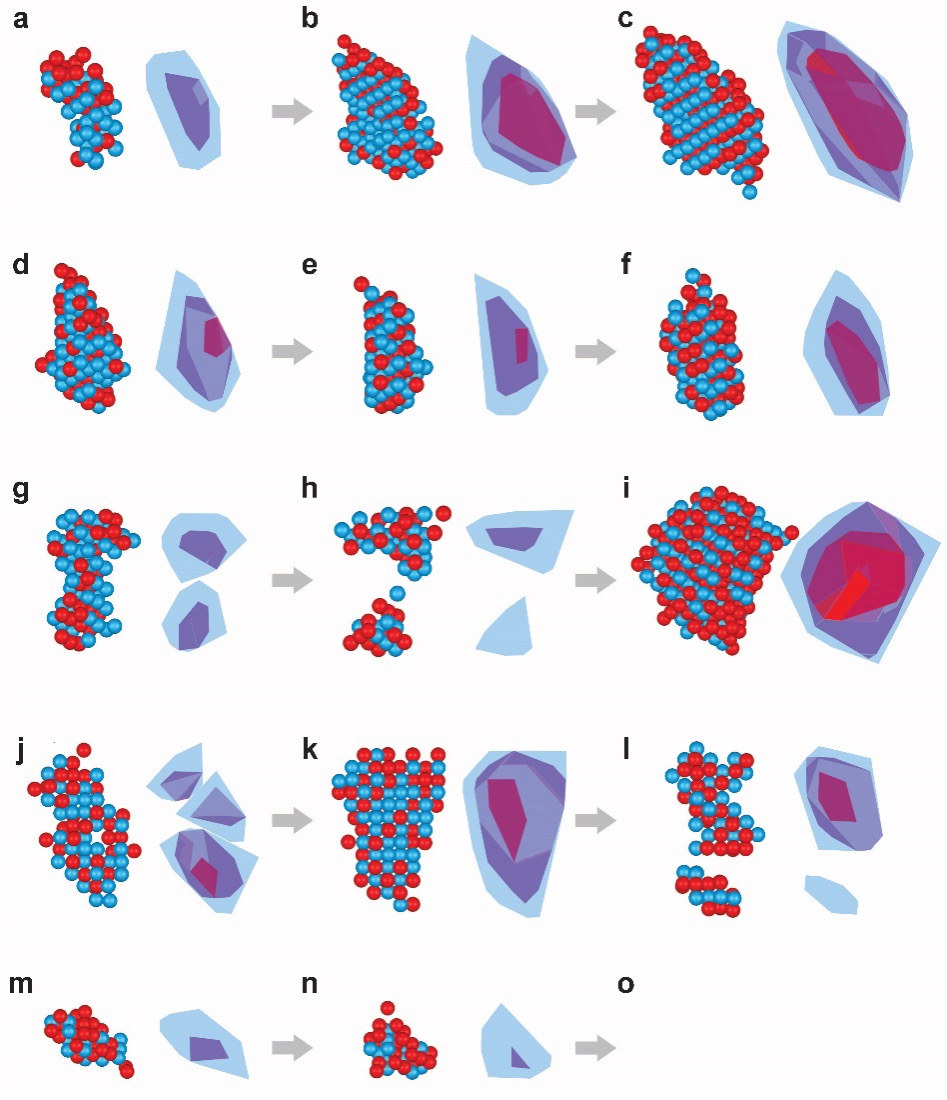
Observing Crystal Nucleation in 4D at Atomic Resolution
8/8/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder) and Jianwei Miao (UCLA)
Nucleation plays a critical role in many physical and biological phenomena, ranging from the formation of clouds to the initiation of neurodegenerative diseases. However, nucleation is a challenging process to study, especially in its early stages.
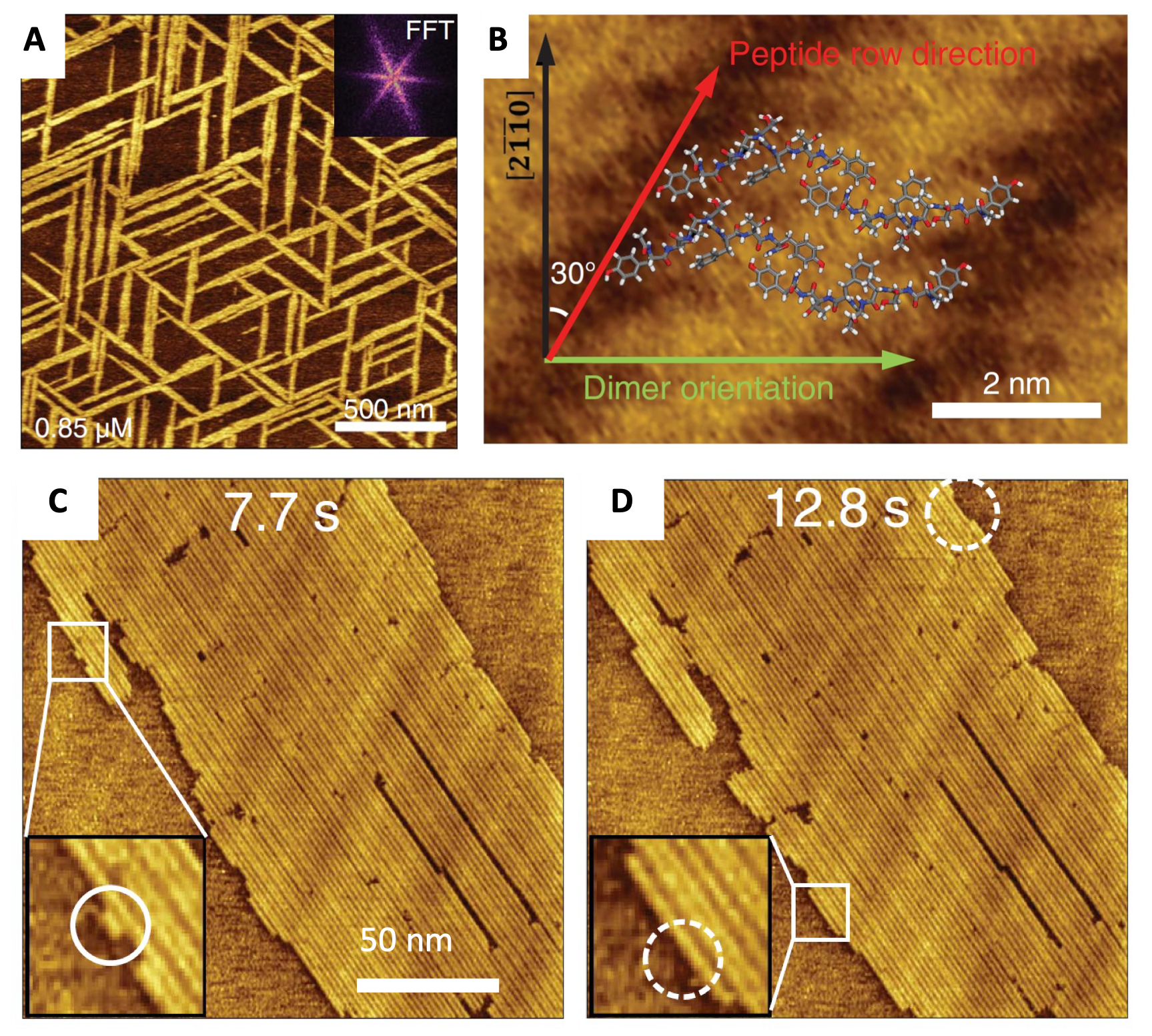
Monitoring the 2D Assembly of Peptides
8/7/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder) and Yu Huang (UCLA)
We identified the mechanism of nucleation and assembly of peptides on 2D layered substrates using a combination of biomimetic synthesis, highly resolved in-situ atomic force microscopy (AFM), and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations.
Deciphering Chemical Order / Disorder at the Single-atom Level
8/7/2024 | Jianwei Miao (UCLA)
Perfect crystals are rare in nature. Real materials often contain crystal defects and chemical order/disorder such as grain boundaries, dislocations, interfaces, surface reconstructions and point defects. Such disruption in periodicity strongly affects material properties and functionality.
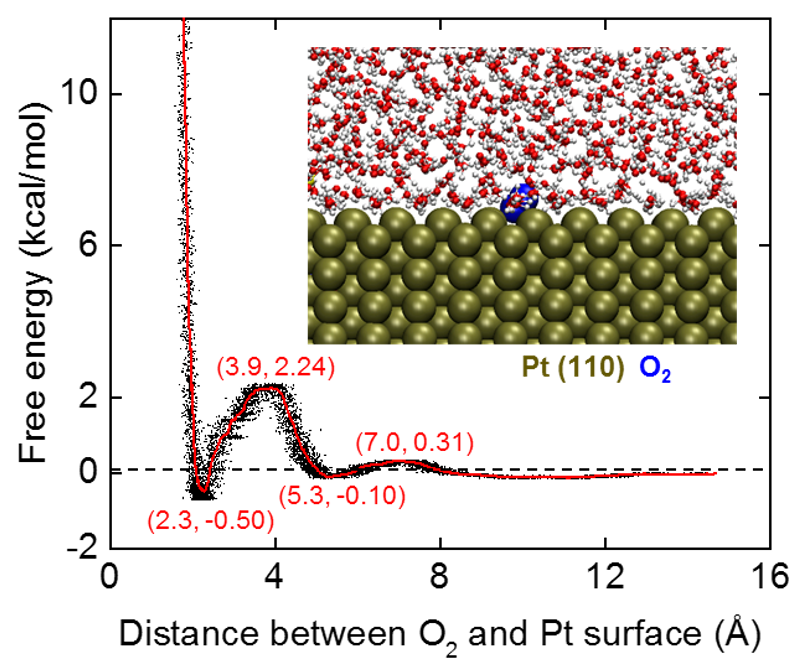
Quantitative Insights into O2 Binding to Pt-M Surfaces
8/7/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder)
We introduced polarizable potentials for metals to accurately reproduce induced charges upon an applied voltage, complete surface/water interfacial properties, and binding of ligands on the 1 to 1000 nm scale. The calculations are a million times faster and partly more accurate than DFT methods (manuscript under review in Nat. Comm.).
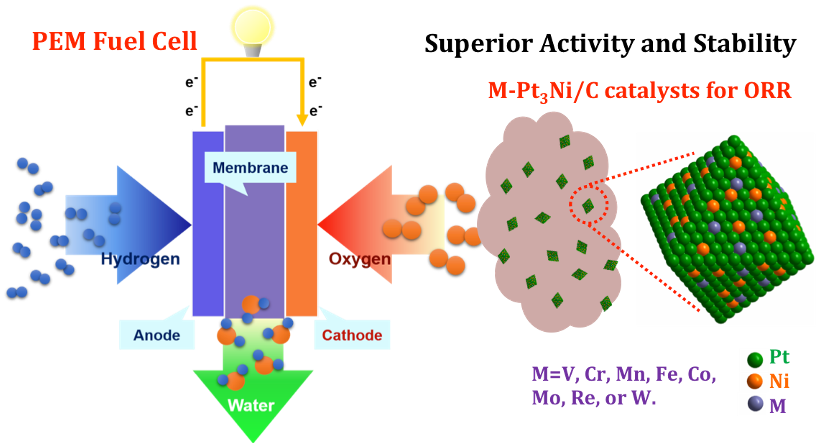
High-performance ORR Catalysts
8/7/2024 | Yu Huang (UCLA)
We have developed a class of highly active and ultra-stable catalysts for oxygen reduction reactions (ORR), by doping the composition of Pt3Ni surface layers with various transition metals (M). Mo-Pt3Ni/C demonstrated ~4 times higher activity than the undoped Pt3Ni/C, and nearly two orders magnitude higher activity than commercial Pt/C, while at the time exhibiting ultra-stability that greatly outperform bothPt3Ni/C and Pt/C.
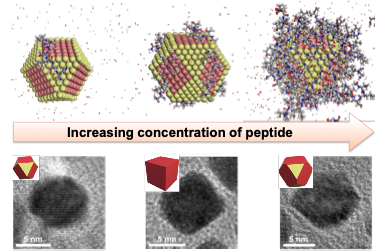
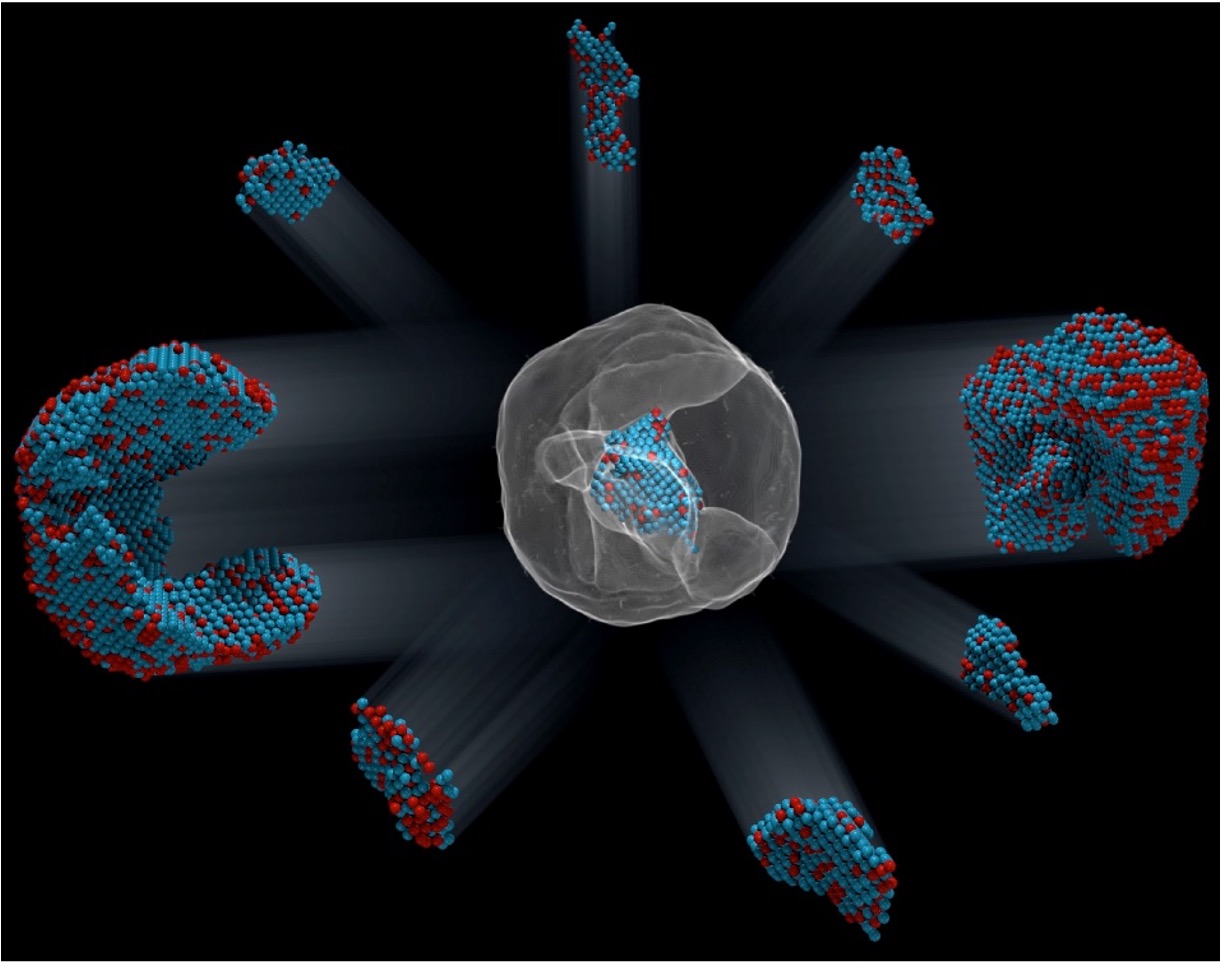
Design of Nanoalloys in 3D Atomic Resolution
8/6/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder) Yu Huang (UCLA)
The mechanism of selective peptide recognition of Pt nanocrystals and peptide-directed growth into specific shapes has been explained using large-scale molecular dynamics simulation and experiment.
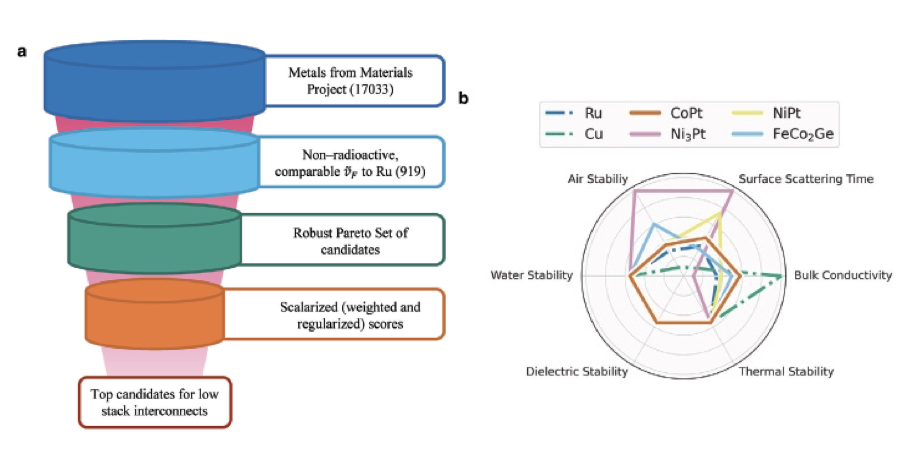
Rapid Identification of Novel Compound Metals for Interconnect Applications
8/2/2024 | F. H. da Jornada (Stanford)
Here, a multi-objective search is developed, combined with first-principles calculations, to rapidly screen over 15,000 materials and discover new interconnect candidates. The approach is validated on one of the identified candidates, CoPt, using both ab initio and experimental transport studies, showcasing its potential to supplant Ru and Cu for future local interconnects.
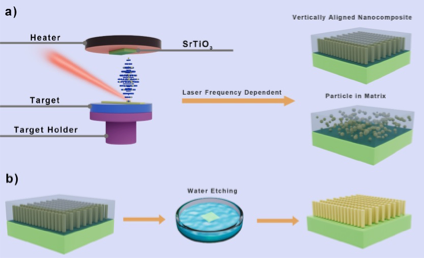
Au Nanopillar Array Prepared by Selective Etching of Au-Sr3Al2O6 Vertically Aligned Nanocomposite Thin Films
6/24/2024 | Haiyan Wang (Purdue University)
These findings provide a novel strategy for tailoring the Au nanostructures and their optical properties while demonstrating on-chip integration for advanced optical device applications.
Showing 81 to 90 of 217