Research Highlights
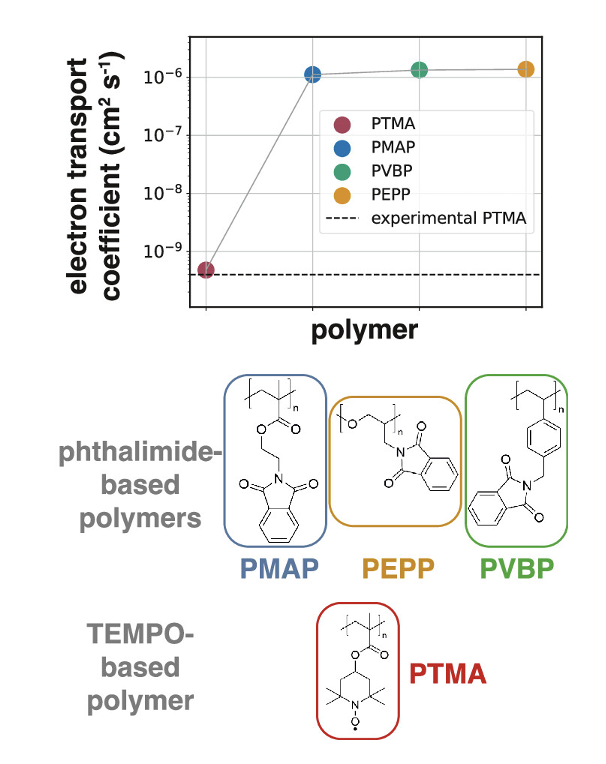
Solid-state Phthalimide-containing Polymers for All-organic Batteries
9/23/2024 | J. Lutkenhaus, D. Tabor (Texas A&M University) S. Rowan, J. De Pablo (U. Chicago)
Redox-active polymers serving as the active materials in solid-state electrodes offer a promising path toward realizing all-organic batteries. While both cathodic and anodic redox-active polymers are needed, the diversity of the available anodic materials is limited. Here, solid-state structural, ionic, and electronic properties of anodic, phthalimide-containing polymers are predicted using a multiscale approach that combines atomistic molecular dynamics, electronic structure calculations, and machine learning surrogate models.
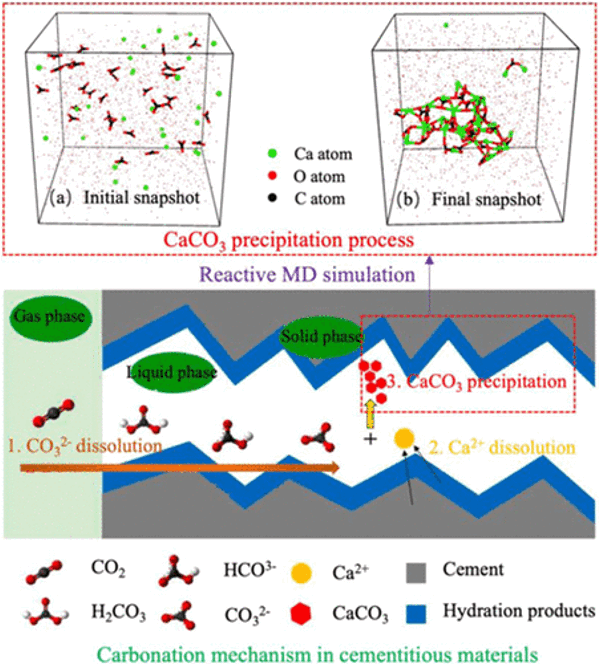
Investigation of Carbonation Kinetics in Carbonated Cementitious Materials by Reactive Molecular Dynamics
9/18/2024 | Mathieu Bauchy and Gaurav Sant (UCLA)
Cement concrete is a calcium-containing material, so it can capture and store carbon dioxide itself mainly via three ways: 1) carbonating the raw materials of cement concrete before concrete preparation, 2) carbonating the fresh concrete during the mixing period of raw materials, and 3) accelerated carbonation curing of cement concrete. Direct carbonation of recycled aggregate can improve its density, reduce water absorption, and improve mechanical properties.
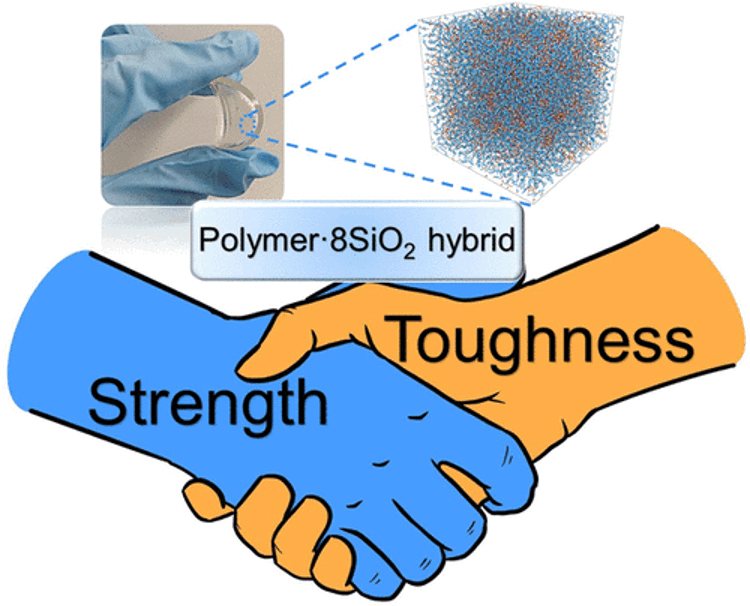
Resolving the Conflict between Strength and Toughness in Bioactive Silica-Polymer Hybrid Materials
9/18/2024 | Mathieu Bauchy (UCLA)
Simultaneously improving the strength and toughness of materials is a major challenge. Inorganic–polymer hybrids offer the potential to combine mechanical properties of a stiff inorganic glass with a flexible organic polymer.
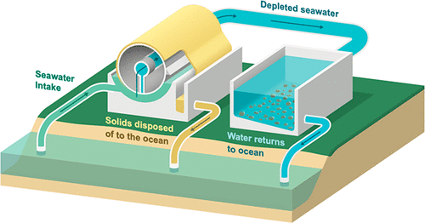
Saline Water-based Mineralization Pathway for Gigatonne-scale CO2 Management
9/18/2024 | Gaurav Sant (UCLA)
Unlike conventional sorbent- or solvent-based CO2 capture processes where substantial energy expenditures are associated with demixing and desorbing CO2, the single-step carbon sequestration and storage (sCS2) approach relies on electrolytic carbonate mineral precipitation using renewable energy within a simple and scalable process design.
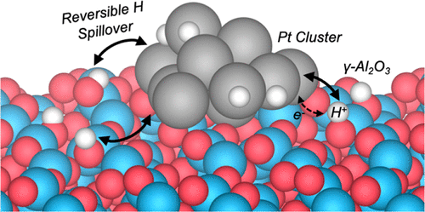
Charge Transfer Drives Hydrogen Adsorption, Spillover, and Hydroxylation
9/17/2024 | Dionisios Vlachos (University of Delaware)
Here, metal−support interactions are explored using hydrogen adsorption on a dehydroxylated γ-Al2O3(110) supported Pt10 cluster as a prototype. Through molecular dynamics simulations performed using an actively trained machine-learned force field, reversible hydrogen spillover was observed between the support and the metal.
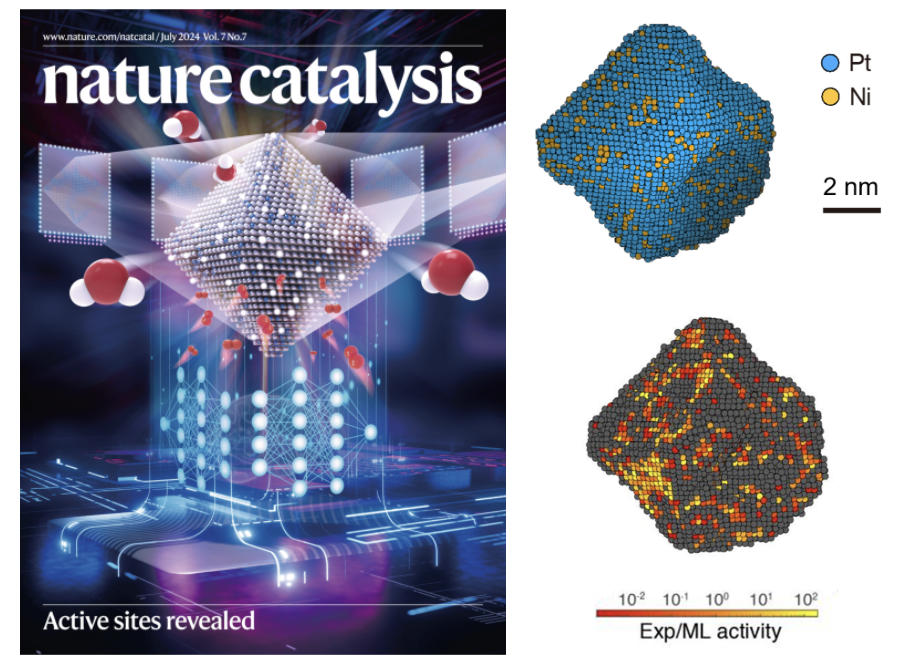
Design and Testing of Nanoalloy Catalysts in 3D Atomic Resolution
8/8/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder) Yu Huang and Jianwei Miao (UCLA)
Heterogeneous catalysts play a key role in the chemical and energy industries. Despite significant progress in theoretical, computational, and experimental studies, identifying the active sites of alloy nanocatalysts remains a major challenge.
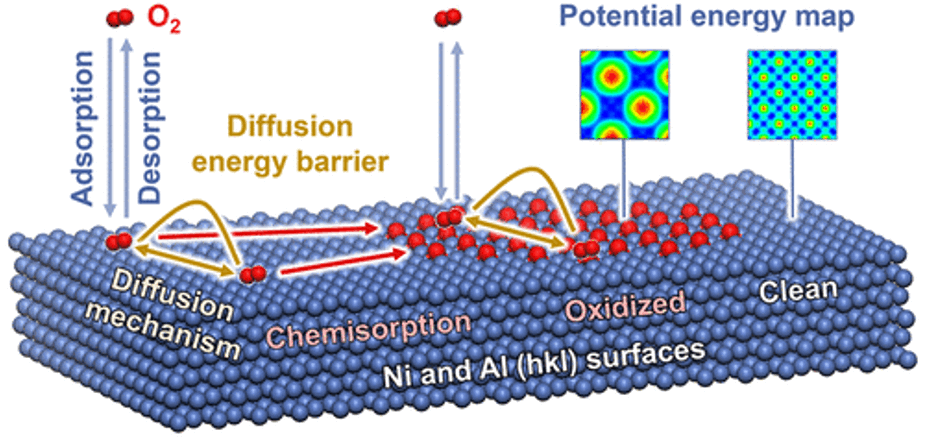
Adsorption and Diffusion of Oxygen on Pure and Partially Oxidized Metal Surfaces in Ultrahigh Resolution
8/8/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder)
The interaction of gas molecules with metal and oxide surfaces plays a critical role in corrosion, catalysis, sensing, and heterogeneous materials. However, insights into the dynamics of O2 from picoseconds to microseconds have remained unavailable to date.
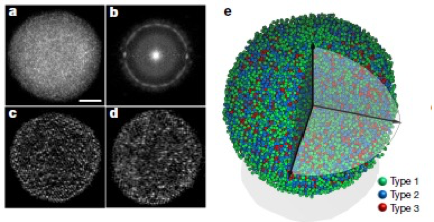
Determining the Three-dimensional Atomic Structure of an Amorphous Solid
8/8/2024 | Jianwei Miao (UCLA)
Amorphous solids such as glass, plastics and amorphous thin films are ubiquitous in our daily life and have broad applications ranging from telecommunications to electronics and solar cells. However, owing to the lack of long-range order, the three-dimensional (3D) atomic structure of amorphous solids has so far eluded direct experimental determination. Here an atomic electron tomography reconstruction method has been developed to experimentally determine the 3D atomic positions of an amorphous solid.

Predicting Surface Reactivity for Biomass Upgrading
8/8/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder)
Ligand-protected metal nanoparticles are widely used in heterogeneous catalysis and biomass upgrading. Thiolate surfactants can greatly improve the overall yield; however, the dynamics of the reacting species and the reaction mechanism have remained unknown at the molecular scale

Interpretable Molecular Models for MoS2
8/8/2024 | Hendrik Heinz (University of Colorado Boulder), J. Miao and Y. Hung (UCLA)
MoS2 is a layered material with outstanding electrical and optical properties. The surface, interfacial, and mechanical properties are important for the design of functional materials and increased control over performance.
Showing 71 to 80 of 217