DMREF Specific Highlights
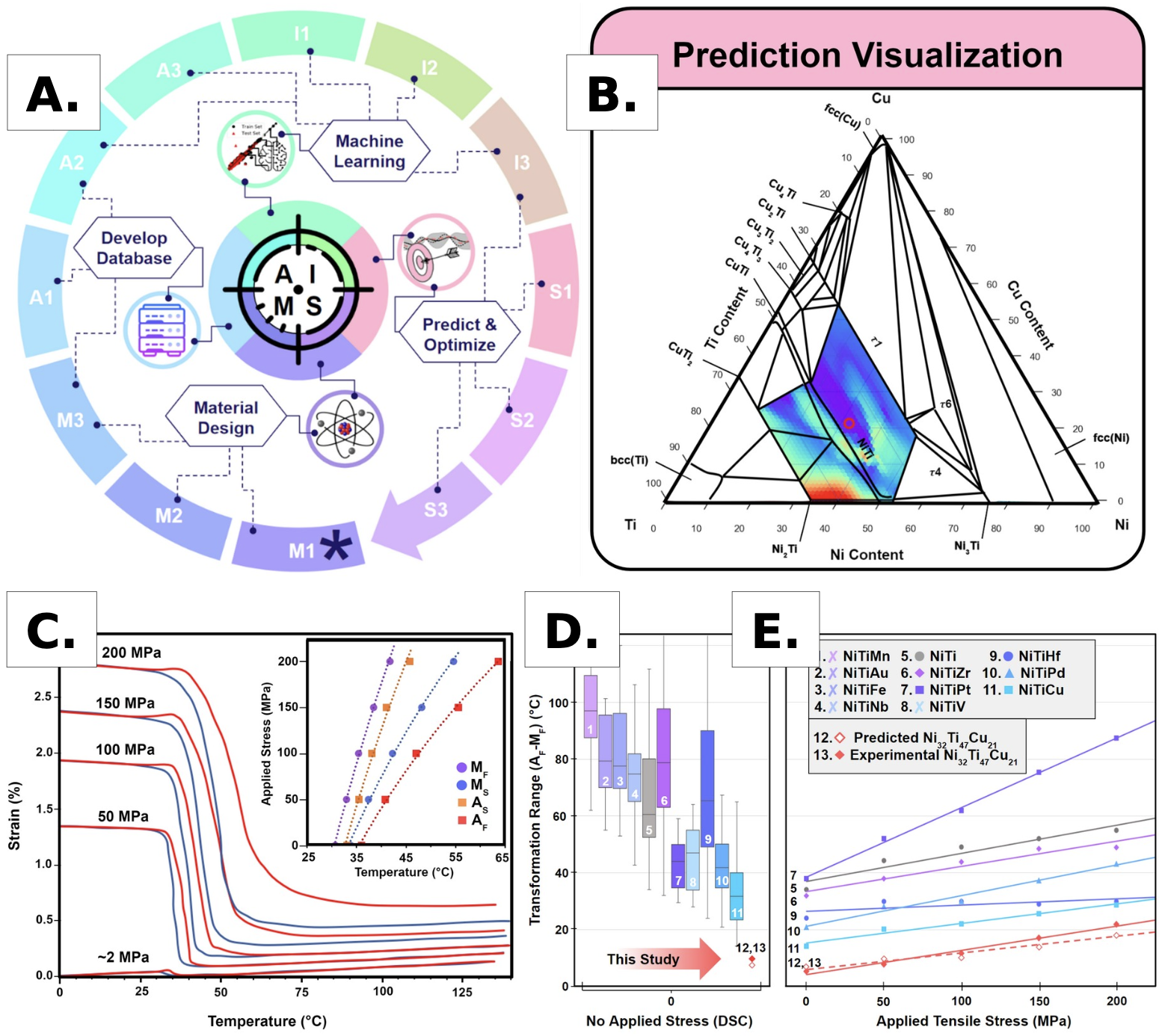
Data-driven Shape Memory Alloy Discovery using Artificial Intelligence Materials Selection (AIMS) Framework
4/1/2022 | W. Trehern, R. Ortiz-Ayala, K. C. Atli, R. Arroyave, I. Karaman
Previous studies have focused on minimizing hysteresis under no stress, but not under applied stress.
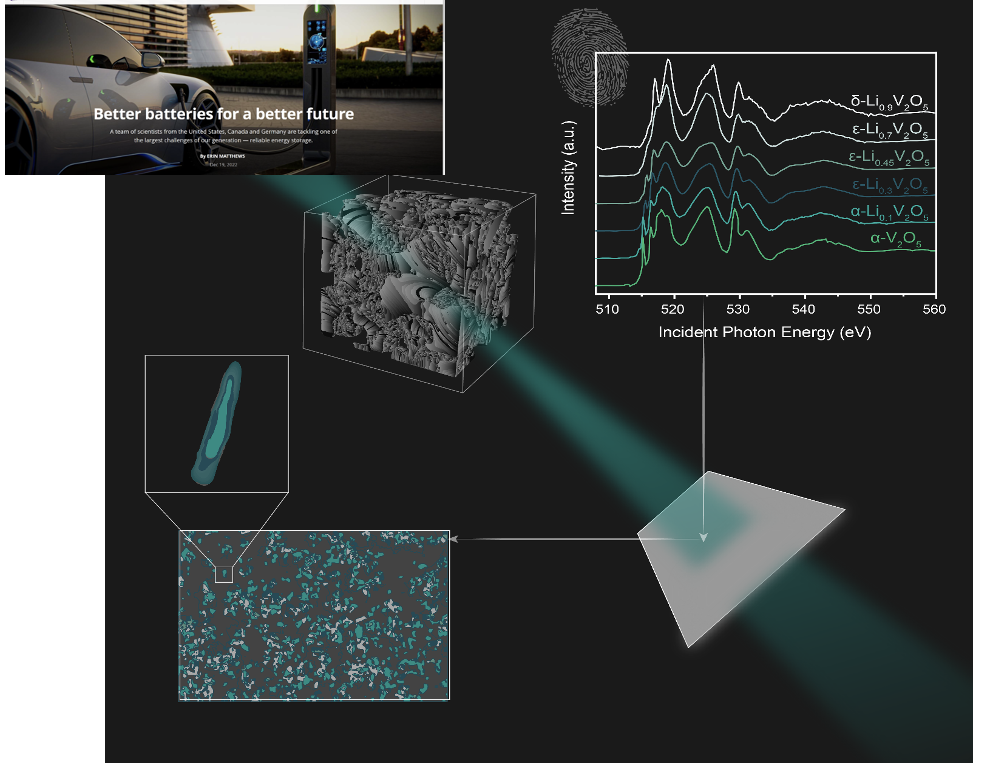
Hyperspectral Data Analytics and Image Analysis Toolsets Across Length Scales
1/1/2022 | Sarbajit Banerjee, Texas A&M University
We have curated a large database of X-ray absorption spectra for phase-pure lithiated transition metal oxides with well-defined lithiation stoichiometries.
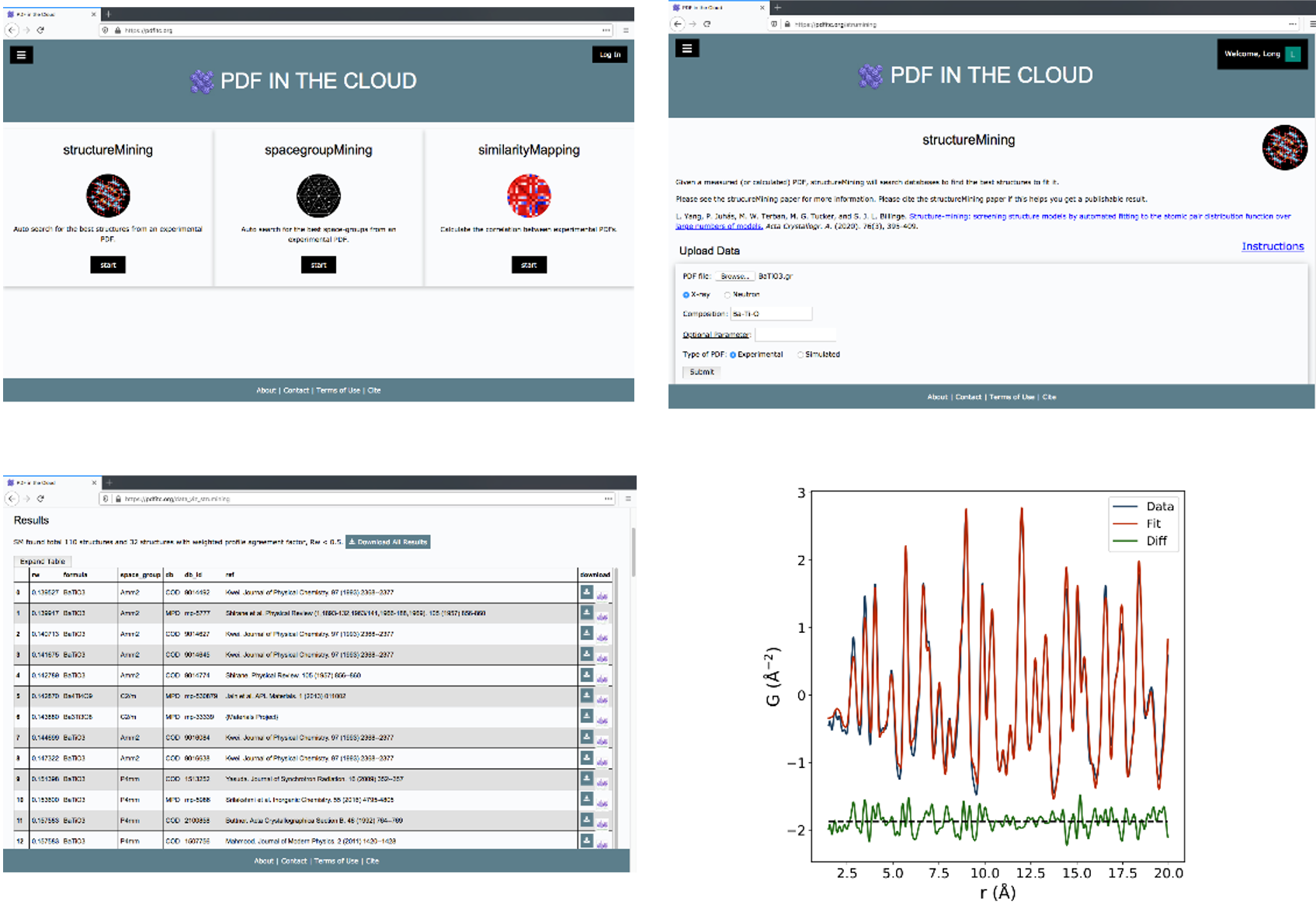
An AI-driven, Cloud-based, Materials Discovery Platform for Nanomaterial Structure: PDFitc
12/3/2021 | S. Billinge, Q. Du, D. Hsu (Columbia U.)
We have developed a cloud-based, AI driven, platform for nanomaterial structure determination: “PDF in the cloud” (PDFitc.org), which consists of various applications for nanostructure determination, including a ML-based classifier for discovering material symmetry from a measured dataset, a high-throughput structure screening tool for predicting the structure of a measured signal, and a data-similarity visualization tool for finding changes in a signal in a time or temperature series.
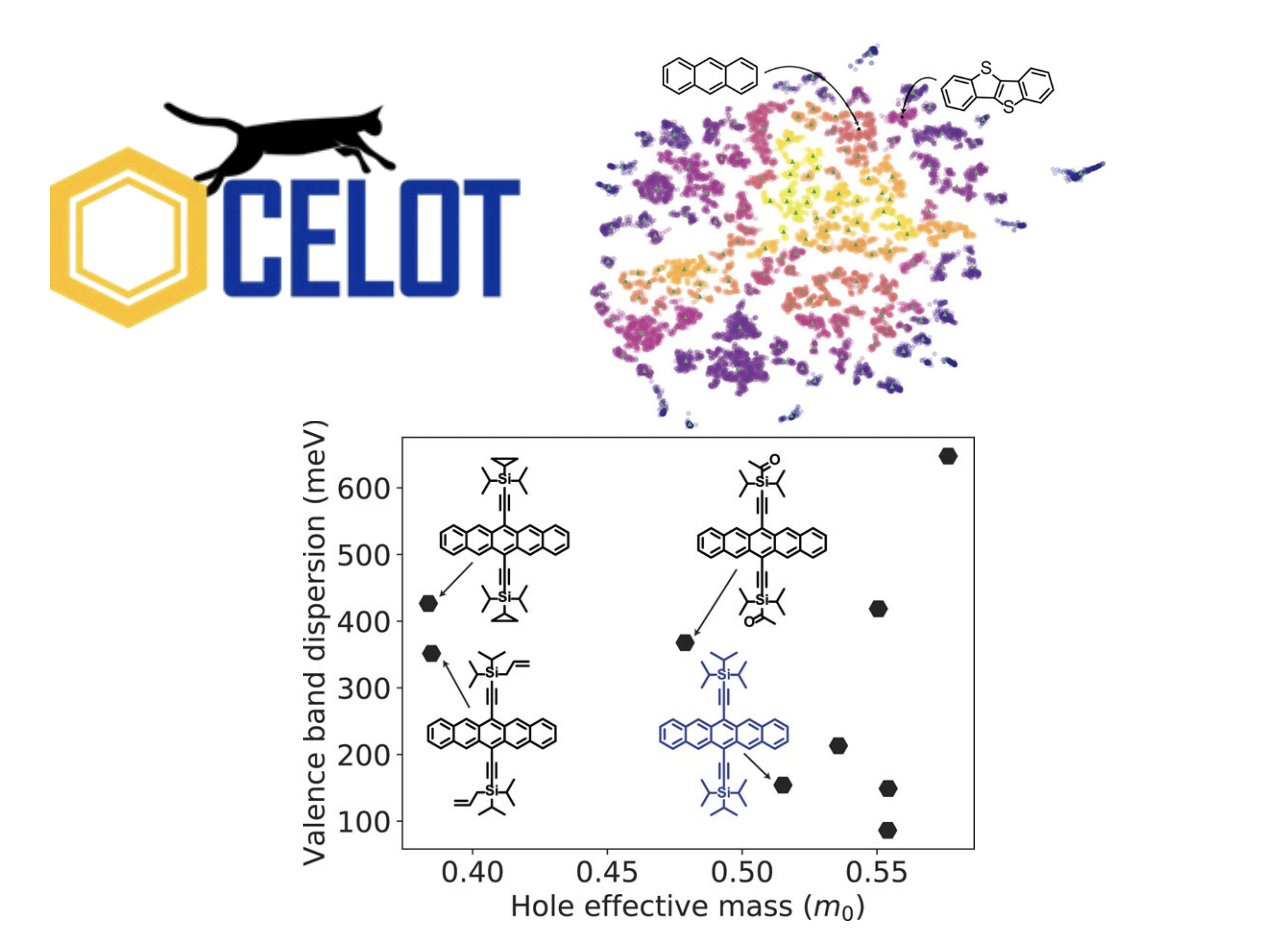
OCELOT: Toward Data-driven Discovery of Organic Semiconductors
4/1/2021 | J. Anthony & C. Risko (U. Kentucky)
While the synthetic chemist can fine tune the chemical structure and architecture of π-conjugated molecules, and in turn the electronic, redox, and optical properties, the performance of organic semiconductors (OSC) are dependent on how these molecular building blocks pack and interact in the solid state.
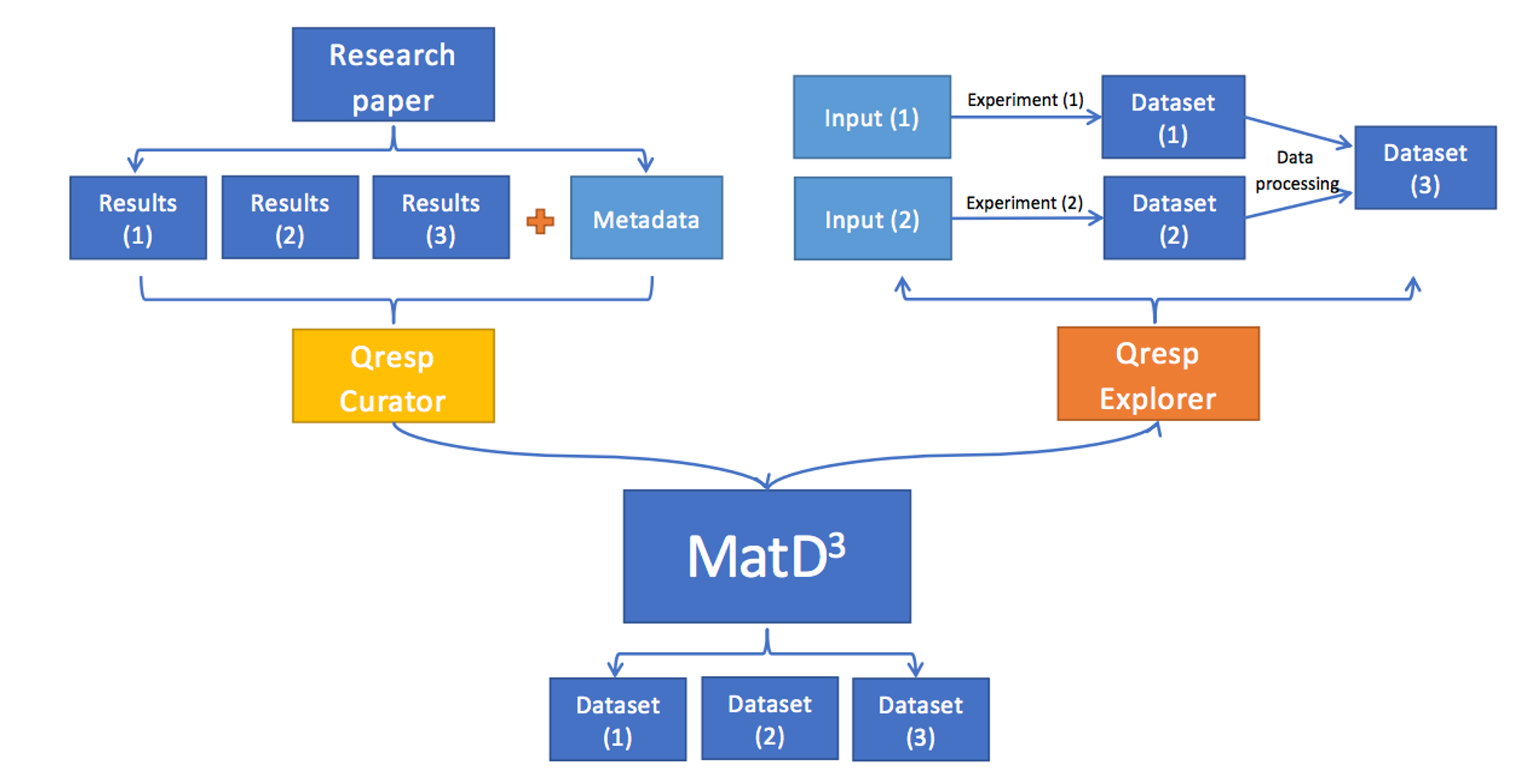
Data Reproducibility and Traceability forCommunity Materials Databases: Qresp for MatD3
1/16/2020 | Volker Blum (Duke University)
The discovery of new materials as well as the determination of a vast set of materials properties for science and technology is a fast-growing field of research, with contributions from many groups worldwide.
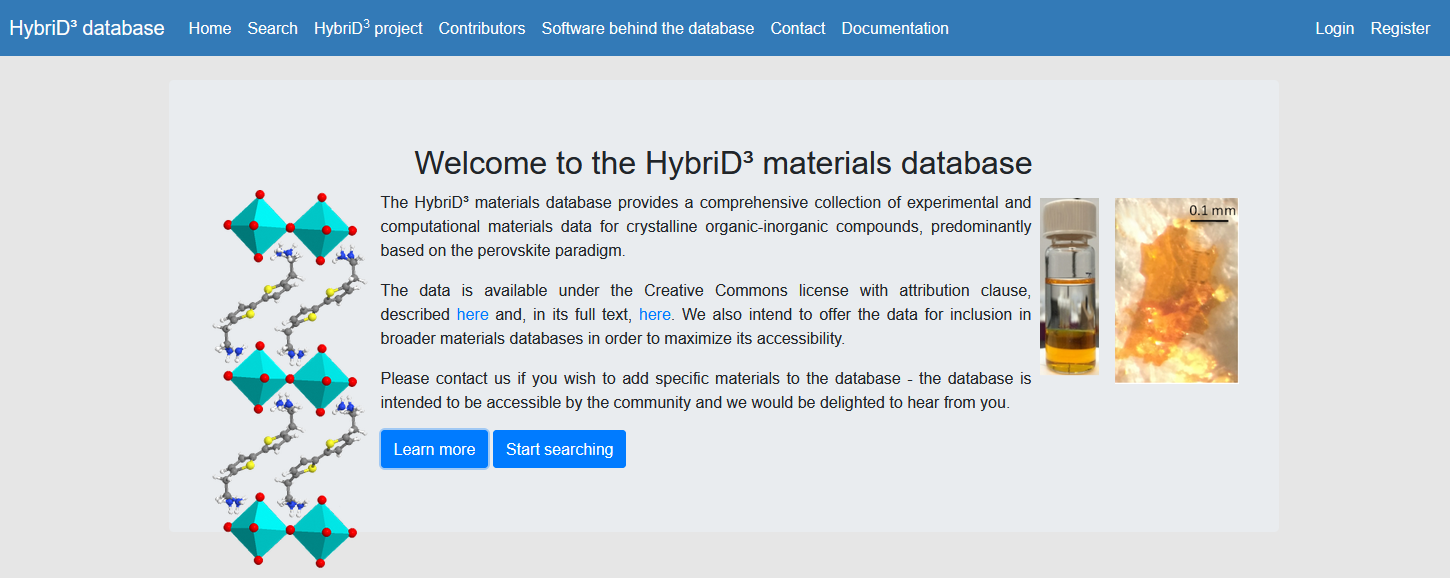
HybriD3 Materials Database
1/16/2020 | Volker Blum, Duke University
MatD3 is intended to provide a simple solution for making diverse datasets available individually and rapidly.
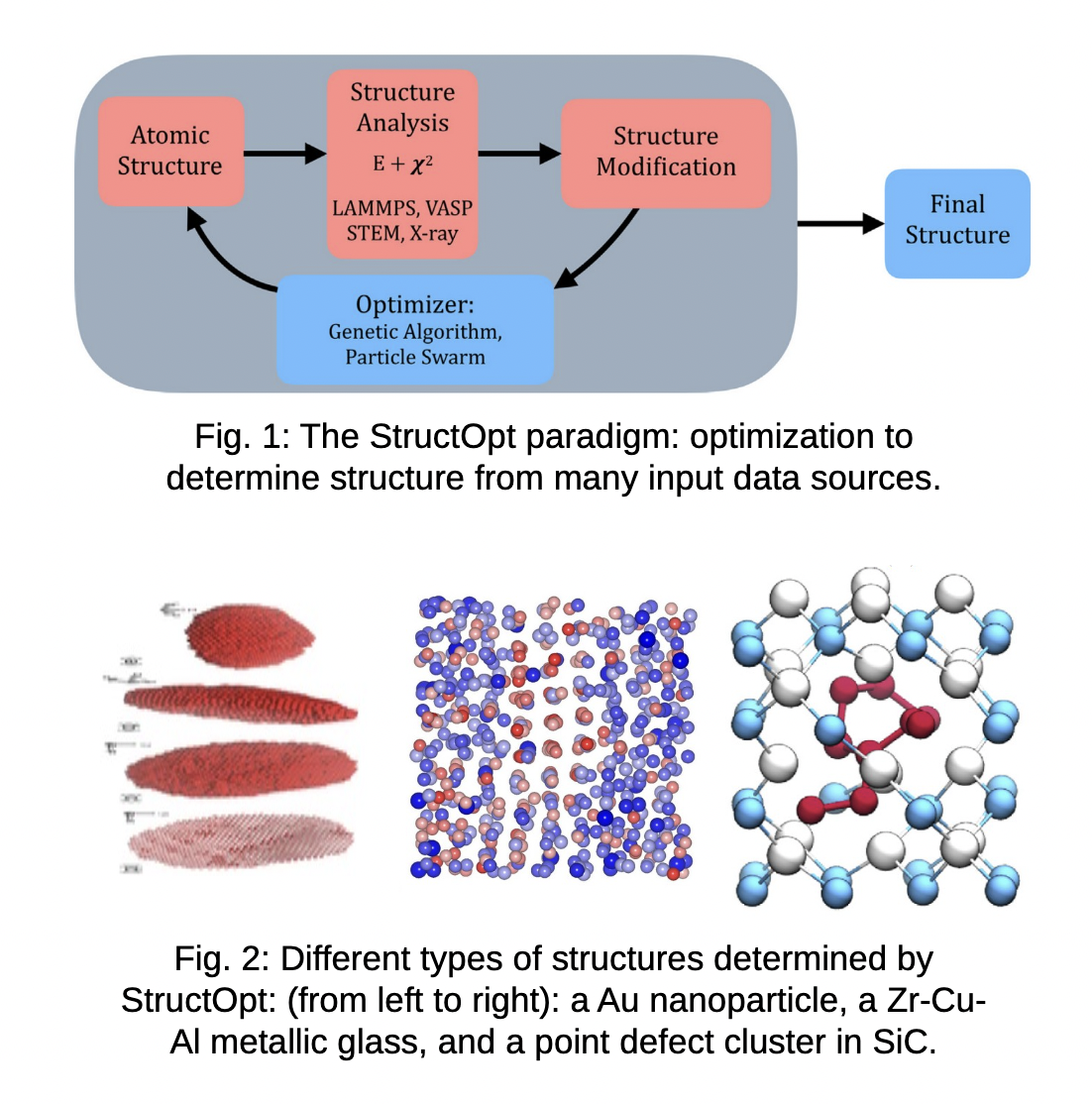
High Throughput Design of Metallic Glasses with Physically Motivated Descriptors
4/1/2019 | Dane Morgan and Paul Voyles (University of Wisconsin)
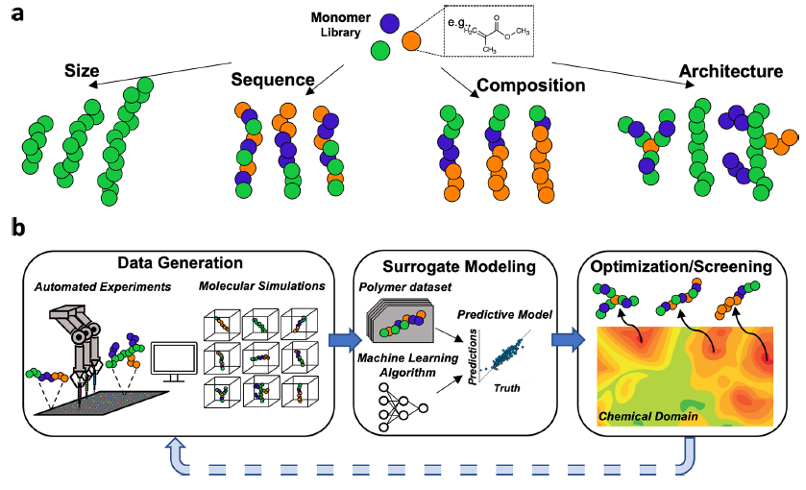
Spotlight: Data Driven Design of Polymer-based Biomaterials
3/20/2018 | Michael Webb (Princeton University)
Polymers, with the capacity to tunably alter properties and response based on manipulation of their chemical characteristics, are attractive components in biomaterials. Nevertheless, their potential as functional materials is also inhibited by their complexity, which complicates rational or brute-force design and realization. In recent years, machine learning has emerged as a useful tool for facilitating materials design via efficient modeling of structure−property relationships in the chemical domain of interest. Here, the emergence of data-driven design of polymers that can be deployed in biomaterials is discussed with particular emphasis on complex copolymer systems.
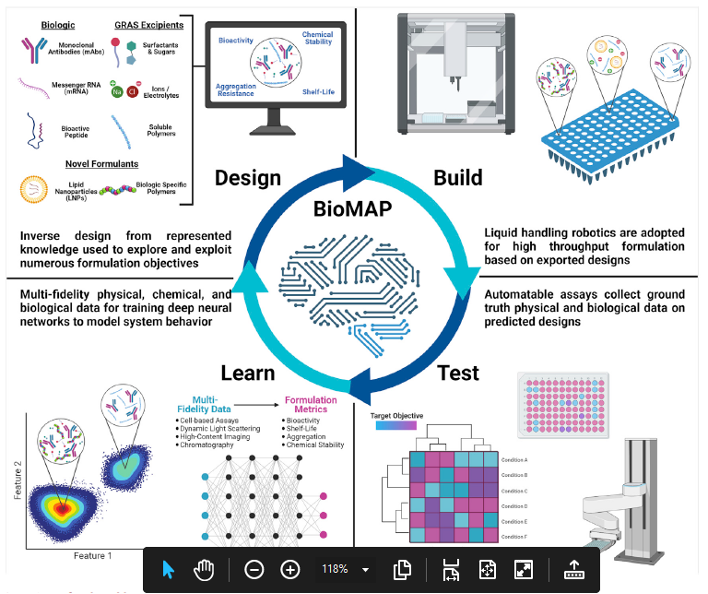
Perspective: Biologic Formulation in a Self-driving Biomaterials Lab
3/20/2018 | Adam Gormley (Rutgers University)
Biologics such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and RNA therapeutics have revolutionized standard of care but present stability challenges due to their fragile structure. This is particularly true considering the demanding manufacturing, storage, distribution, and administration requirements that far exceed the otherwise stable biological environment from which they are derived.
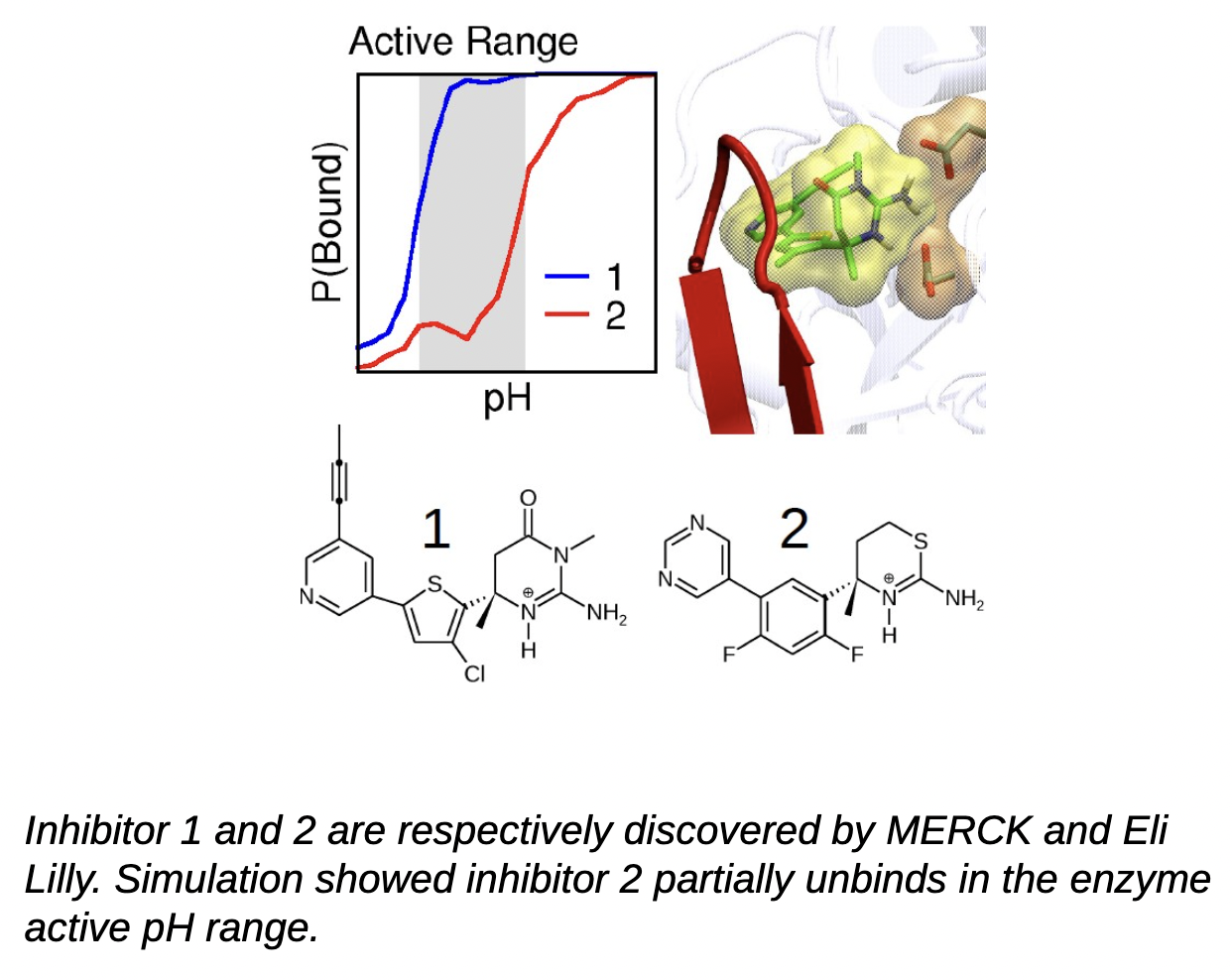
Industrial Collaboration:pH-responsive Inhibitors
2/23/2016 | Jana Shen
Targeting β -secretase (BACE1) with small-molecule inhibitors offers a promising route for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. However, the intricate pH dependence of BACE1 function and inhibitor efficacy has posed a major challenge for structure-based drug design.
Showing 31 to 40 of 40